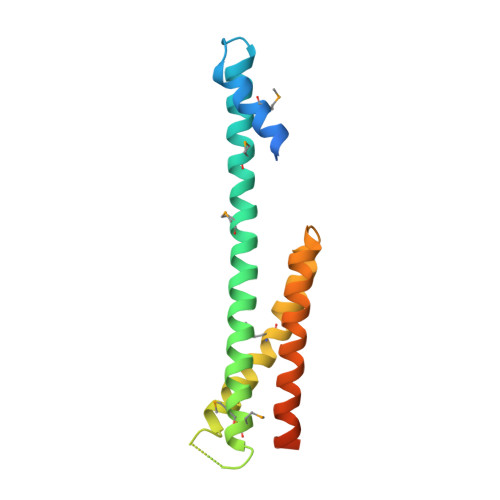
The Structure of the GGA1-GAT Domain Reveals the Molecular Basis for ARF Binding and Membrane Association of GGAs
Collins, B.M., Watson, P.J., Owen, D.J.(2003) Dev Cell 4: 321-332
- PubMed: 12636914
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00037-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NAF - PubMed Abstract:
The GGAs are a family of clathrin adaptor proteins involved in vesicular transport between the trans-Golgi network and endosomal system. Here we confirm reports that GGAs are targeted to the Golgi via interaction between the GGA-GAT domain and ARF-GTP, and we present the structure of the GAT domain of human GGA1, completing the structural description of the folded domains of GGA proteins. The GGA-GAT domain possesses an all alpha-helical fold with a "paper clip" topology comprising two independent subdomains. Structure-based mutagenesis demonstrates that ARF1-GTP binding by GGAs is exclusively governed by the N-terminal "hook" subdomain, and, using an in vitro recruitment assay, we show that ARF-GTP binding by this small structure is required and sufficient for Golgi targeting of GGAs.
- Department of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, CB2 2XY, Cambridge, United Kingdom. bmc25@cam.ac.uk
Organizational Affiliation: