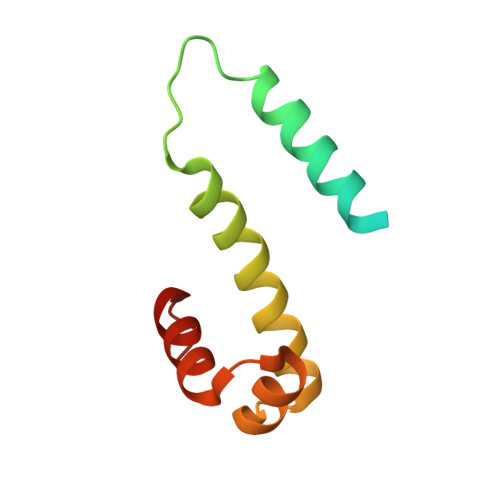
The structure of Fis mutant Pro61Ala illustrates that the kink within the long alpha-helix is not due to the presence of the proline residue.
Yuan, H.S., Wang, S.S., Yang, W.Z., Finkel, S.E., Johnson, R.C.(1994) J Biological Chem 269: 28947-28954
- PubMed: 7961857
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb1fip/pdb
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FIP - PubMed Abstract:
The influence of proline on bending of the alpha-helix was investigated by replacement of the proline residue located in the middle of the long alpha-helix of the Fis protein with alanine, serine, or leucine. Each of the three substitutions folded into a stable protein with the same or higher melting points than the wild-type, but only Pro61Ala was functionally active in stimulating Hin-mediated DNA inversion. Pro61Ala formed crystals that were isomorphous with the wild-type protein allowing the structure to be determined at 1.9-A resolution by x-ray diffraction methods. The structure of the Pro61Ala mutant is almost identical to the wild-type protein, consistent with its near wild-type activity. One of the alpha-helices, the B-helix, is kinked in the wild-type Fis protein by 20 degrees which was previously assumed to be caused solely by the presence of proline 61 in the center of the helix. However, the B-helix is still kinked by 16 degrees when proline 61 is replaced by alanine. Local peptide backbone movement around residue 57 adjusts the geometry of the helix to accommodate the new main chain hydrogen bond between the -CO group in Glu57 and the -NH group in Ala61. Thus, the kink of the alpha-helix in Pro61Ala does not require the presence of proline.
- Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China.
Organizational Affiliation: