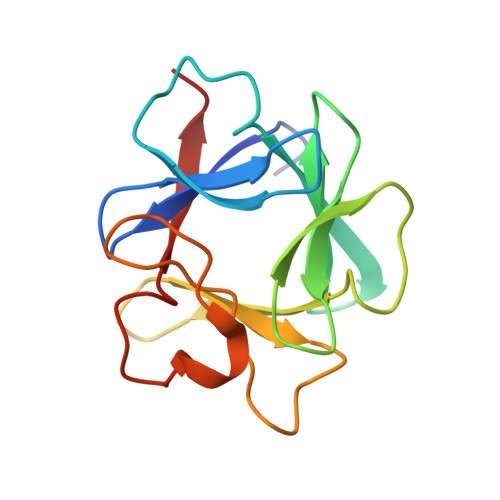
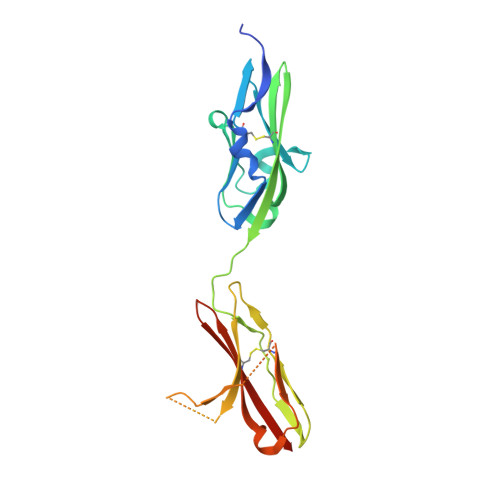
Crystal structures of two FGF-FGFR complexes reveal the determinants of ligand-receptor specificity.
Plotnikov, A.N., Hubbard, S.R., Schlessinger, J., Mohammadi, M.(2000) Cell 101: 413-424
- PubMed: 10830168
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80851-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EV2, 1EVT - PubMed Abstract:
To elucidate the structural determinants governing specificity in fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling, we have determined the crystal structures of FGF1 and FGF2 complexed with the ligand binding domains (immunoglobulin-like domains 2 [D2] and 3 [D3]) of FGF receptor 1 (FGFR1) and FGFR2, respectively. Highly conserved FGF-D2 and FGF-linker (between D2-D3) interfaces define a general binding site for all FGF-FGFR complexes. Specificity is achieved through interactions between the N-terminal and central regions of FGFs and two loop regions in D3 that are subject to alternative splicing. These structures provide a molecular basis for FGF1 as a universal FGFR ligand and for modulation of FGF-FGFR specificity through primary sequence variations and alternative splicing.
- Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, New York 10016, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: