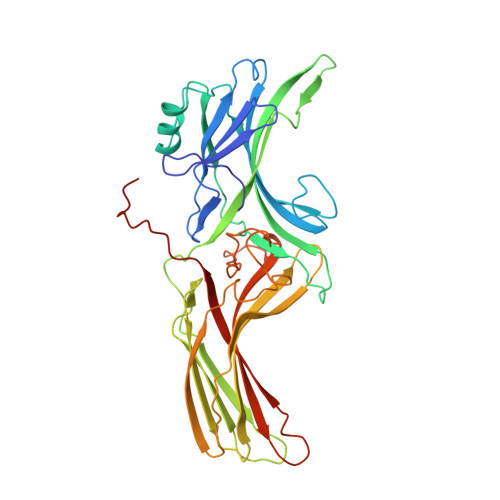
X-ray crystal structure of arrestin from bovine rod outer segments.
Granzin, J., Wilden, U., Choe, H.W., Labahn, J., Krafft, B., Buldt, G.(1998) Nature 391: 918-921
- PubMed: 9495348
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/36147
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1AYR - PubMed Abstract:
Retinal arrestin is the essential protein for the termination of the light response in vertebrate rod outer segments. It plays an important role in quenching the light-induced enzyme cascade by its ability to bind to phosphorylated light-activated rhodopsin (P-Rh*). Arrestins are found in various G-protein-coupled amplification cascades. Here we report on the three-dimensional structure of bovine arrestin (relative molecular mass, 45,300) at 3.3 A resolution. The crystal structure comprises two domains of antiparallel beta-sheets connected through a hinge region and one short alpha-helix on the back of the amino-terminal fold. The binding region for phosphorylated light-activated rhodopsin is located at the N-terminal domain, as indicated by the docking of the photoreceptor to the three-dimensional structure of arrestin. This agrees with the interpretation of binding studies on partially digested and mutated arrestin.
- Forschungszentrum Jülich, Institut für Biologische Informationsverarbeitung, Germany. J.Granzin@fz-juelich.de
Organizational Affiliation: