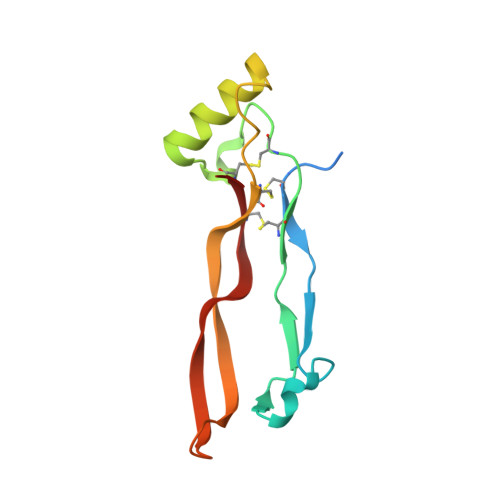
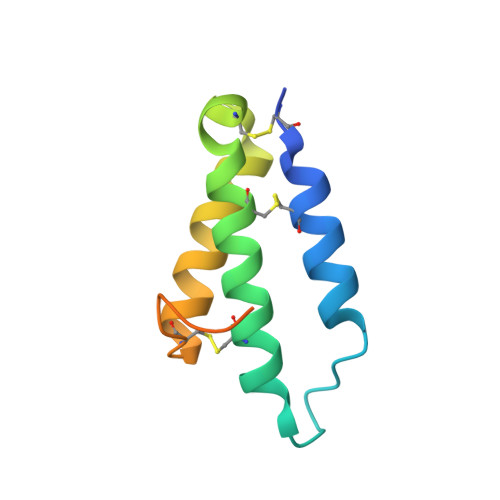
Repulsive guidance molecules lock growth differentiation factor 5 in an inhibitory complex.
Malinauskas, T., Peer, T.V., Bishop, B., Mueller, T.D., Siebold, C.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 15620-15631
- PubMed: 32576689
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2000561117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Z3G, 6Z3H, 6Z3J, 6Z3L, 6Z3M - PubMed Abstract:
Repulsive guidance molecules (RGMs) are cell surface proteins that regulate the development and homeostasis of many tissues and organs, including the nervous, skeletal, and immune systems. They control fundamental biological processes, such as migration and differentiation by direct interaction with the Neogenin (NEO1) receptor and function as coreceptors for the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/growth differentiation factor (GDF) family. We determined crystal structures of all three human RGM family members in complex with GDF5, as well as the ternary NEO1-RGMB-GDF5 assembly. Surprisingly, we show that all three RGMs inhibit GDF5 signaling, which is in stark contrast to RGM-mediated enhancement of signaling observed for other BMPs, like BMP2. Despite their opposite effect on GDF5 signaling, RGMs occupy the BMP type 1 receptor binding site similar to the observed interactions in RGM-BMP2 complexes. In the NEO1-RGMB-GDF5 complex, RGMB physically bridges NEO1 and GDF5, suggesting cross-talk between the GDF5 and NEO1 signaling pathways. Our crystal structures, combined with structure-guided mutagenesis of RGMs and BMP ligands, binding studies, and cellular assays suggest that RGMs inhibit GDF5 signaling by competing with GDF5 type 1 receptors. While our crystal structure analysis and in vitro binding data initially pointed towards a simple competition mechanism between RGMs and type 1 receptors as a possible basis for RGM-mediated GDF5 inhibition, further experiments utilizing BMP2-mimicking GDF5 variants clearly indicate a more complex mechanism that explains how RGMs can act as a functionality-changing switch for two structurally and biochemically similar signaling molecules.
- Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, OX3 7BN Oxford, United Kingdom; tomas@strubi.ox.ac.uk mueller@biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de christian@strubi.ox.ac.uk.
Organizational Affiliation: