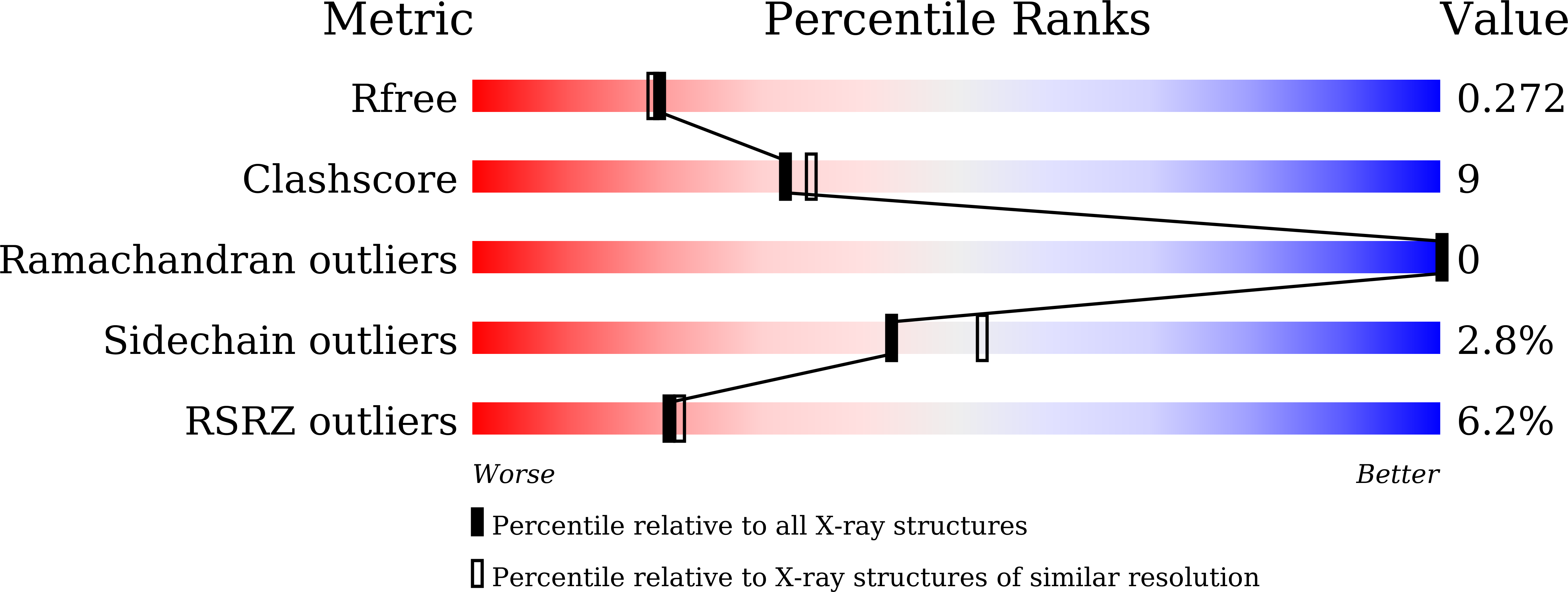
The Mevalonate Pathway Is a Druggable Target for Vaccine Adjuvant Discovery.
Xia, Y., Xie, Y., Yu, Z., Xiao, H., Jiang, G., Zhou, X., Yang, Y., Li, X., Zhao, M., Li, L., Zheng, M., Han, S., Zong, Z., Meng, X., Deng, H., Ye, H., Fa, Y., Wu, H., Oldfield, E., Hu, X., Liu, W., Shi, Y., Zhang, Y.(2018) Cell 175: 1059-1073.e21
- PubMed: 30270039
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.070
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YGI - PubMed Abstract:
Motivated by the clinical observation that interruption of the mevalonate pathway stimulates immune responses, we hypothesized that this pathway may function as a druggable target for vaccine adjuvant discovery. We found that lipophilic statin drugs and rationally designed bisphosphonates that target three distinct enzymes in the mevalonate pathway have potent adjuvant activities in mice and cynomolgus monkeys. These inhibitors function independently of conventional "danger sensing." Instead, they inhibit the geranylgeranylation of small GTPases, including Rab5 in antigen-presenting cells, resulting in arrested endosomal maturation, prolonged antigen retention, enhanced antigen presentation, and T cell activation. Additionally, inhibiting the mevalonate pathway enhances antigen-specific anti-tumor immunity, inducing both Th1 and cytolytic T cell responses. As demonstrated in multiple mouse cancer models, the mevalonate pathway inhibitors are robust for cancer vaccinations and synergize with anti-PD-1 antibodies. Our research thus defines the mevalonate pathway as a druggable target for vaccine adjuvants and cancer immunotherapies.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, China; Joint Graduate Program of Peking-Tsinghua-NIBS, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, China.