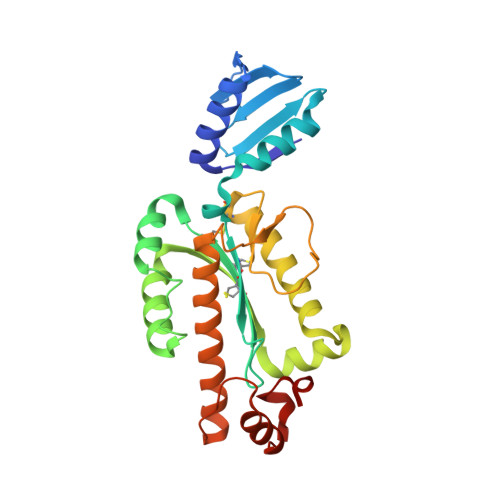
Structure and characterization of RNase H3 from Aquifex aeolicus
Jongruja, N., You, D.J., Angkawidjaja, C., Kanaya, E., Koga, Y., Kanaya, S.(2012) FEBS J 279: 2737-2753
- PubMed: 22686566
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08657.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VN5 - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of ribonuclease H3 from Aquifex aeolicus (Aae-RNase H3) was determined at 2.0 Å resolution. Aae-RNase H3 consists of an N-terminal TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-like domain (N-domain) and a C-terminal RNase H domain (C-domain). The structure of the C-domain highly resembles that of Bacillus stearothermophilus RNase H3 (Bst-RNase H3), except that it contains three disulfide bonds, and the fourth conserved glutamate residue of the Asp-Glu-Asp-Glu active site motif (Glu198) is located far from the active site. These disulfide bonds were shown to contribute to hyper-stabilization of the protein. Non-conserved Glu194 was identified as the fourth active site residue. The structure of the N-domain without the C-domain also highly resembles that of Bst-RNase H3. However, the arrangement of the N-domain relative to the C-domain greatly varies for these proteins because of the difference in the linker size between the domains. The linker of Bst-RNase H3 is relatively long and flexible, while that of Aae-RNase H3 is short and assumes a helix formation. Biochemical characterizations of Aae-RNase H3 and its derivatives without the N- or C-domain or with a mutation in the N-domain indicate that the N-domain of Aae-RNase H3 is important for substrate binding, and uses the flat surface of the β-sheet for substrate binding. However, this surface is located far from the active site and on the opposite side to the active site. We propose that the N-domain of Aae-RNase H3 is required for initial contact with the substrate. The resulting complex may be rearranged such that only the C-domain forms a complex with the substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Material and Life Science, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka, Japan.