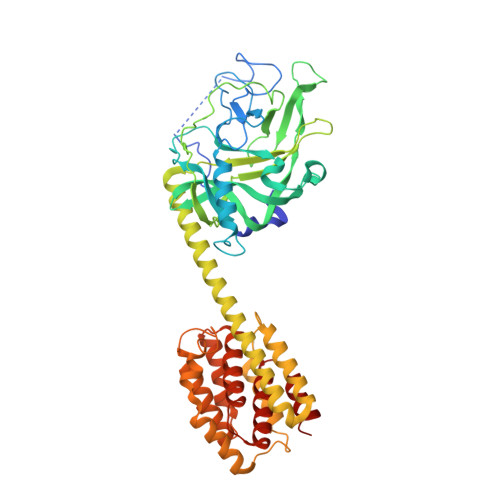
Crystal structure of the cytotoxic bacterial protein colicin B at 2.5 A resolution
Hilsenbeck, J.L., Park, H., Chen, G., Youn, B., Postle, K., Kang, C.(2004) Mol Microbiol 51: 711-720
- PubMed: 14731273
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03884.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RH1 - PubMed Abstract:
Colicin B (55 kDa) is a cytotoxic protein that recognizes the outer membrane transporter, FepA, as a receptor and, after gaining access to the cytoplasmic membranes of sensitive Escherichia coli cells, forms a pore that depletes the electrochemical potential of the membrane and ultimately results in cell death. To begin to understand the series of dynamic conformational changes that must occur as colicin B translocates from outer membrane to cytoplasmic membrane, we report here the crystal structure of colicin B at 2.5 A resolution. The crystal belongs to the space group C2221 with unit cell dimensions a = 132.162 A, b = 138.167 A, c = 106.16 A. The overall structure of colicin B is dumbbell shaped. Unlike colicin Ia, the only other TonB-dependent colicin crystallized to date, colicin B does not have clearly structurally delineated receptor-binding and translocation domains. Instead, the unique N-terminal lobe of the dumbbell contains both domains and consists of a large (290 residues), mostly beta-stranded structure with two short alpha-helices. This is followed by a single long ( approximately 74 A) helix that connects the N-terminal domain to the C-terminal pore-forming domain, which is composed of 10 alpha-helices arranged in a bundle-type structure, similar to the pore-forming domains of other colicins. The TonB box sequence at the N-terminus folds back to interact with the N-terminal lobe of the dumbbell and leaves the flanking sequences highly disordered. Comparison of sequences among many colicins has allowed the identification of a putative receptor-binding domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and School of Molecular Biosciences, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164, USA.