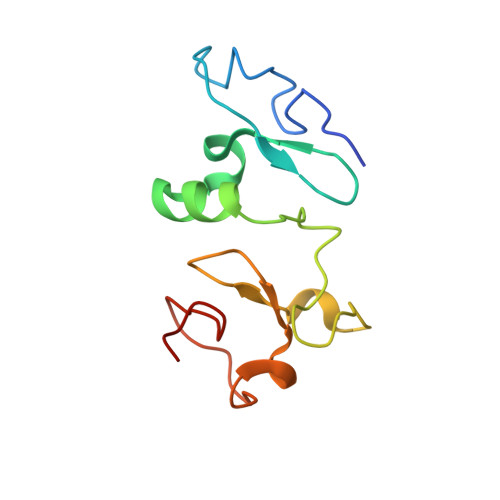
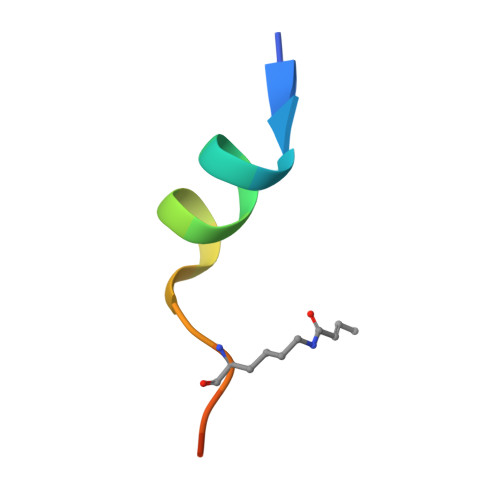
Histone H3K23-specific acetylation by MORF is coupled to H3K14 acylation.
Klein, B.J., Jang, S.M., Lachance, C., Mi, W., Lyu, J., Sakuraba, S., Krajewski, K., Wang, W.W., Sidoli, S., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Warfield, B.M., Kueh, A.J., Voss, A.K., Thomas, T., Garcia, B.A., Liu, W.R., Strahl, B.D., Kono, H., Li, W., Shi, X., Cote, J., Kutateladze, T.G.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 4724-4724
- PubMed: 31624313
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12551-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OIE - PubMed Abstract:
Acetylation of histone H3K23 has emerged as an essential posttranslational modification associated with cancer and learning and memory impairment, yet our understanding of this epigenetic mark remains insufficient. Here, we identify the native MORF complex as a histone H3K23-specific acetyltransferase and elucidate its mechanism of action. The acetyltransferase function of the catalytic MORF subunit is positively regulated by the DPF domain of MORF (MORF DPF ). The crystal structure of MORF DPF in complex with crotonylated H3K14 peptide provides mechanistic insight into selectivity of this epigenetic reader and its ability to recognize both histone and DNA. ChIP data reveal the role of MORF DPF in MORF-dependent H3K23 acetylation of target genes. Mass spectrometry, biochemical and genomic analyses show co-existence of the H3K23ac and H3K14ac modifications in vitro and co-occupancy of the MORF complex, H3K23ac, and H3K14ac at specific loci in vivo. Our findings suggest a model in which interaction of MORF DPF with acylated H3K14 promotes acetylation of H3K23 by the native MORF complex to activate transcription.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, 80045, USA.