Structural Analysis of Cassiicolin, a Host-selective Protein Toxin from Corynespora cassiicola
Barthe, P., Pujade-Renaud, V., Breton, F., Gargani, D., Thai, R., Roumestand, C., de Lamotte, F.(2007) J Mol Biology 367: 89-101
- PubMed: 17234212
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.086
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HGO - PubMed Abstract:
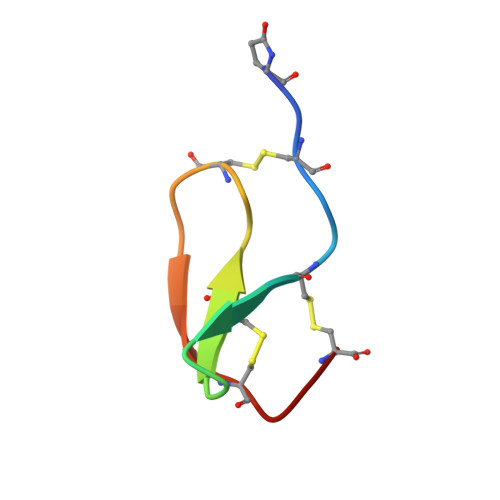
Cassiicolin is a host-selective toxin (HST) produced by the fungus Corynespora cassiicola (strain CCP). It is responsible for the Corynespora leaf fall (CLF) disease, which is among the main pathologies affecting rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Working on purified cassiicolin and using electron microscopy, we have demonstrated that this 27-residue O-glycosylated protein is able to induce cellular damages identical to those induced by the fungus on rubber tree leaves and displays the same host selectivity. The solution structure and disulfide pairing of cassiicolin have been determined using NMR spectroscopy and simulated annealing calculations. Cassiicolin appears to have an original structure with a prolate ellipsoid shape. It adopts an over-all fold consisting of three strands arranged in a right-handed twisted, antiparallel beta-sheet knitted by three disulfide bonds. Its conformation resembles that found in small trypsine-like inhibitors isolated from the brain, the fat body and the hemolymph of locust grasshoppers. But cassiicolin has no sequence homology with these protease inhibitors, and lacks their characteristic substrate-binding loop. Probably, this motif represents one of the few highly stabilized "minimal" scaffolds, with a high sequence permissiveness, that nature has selected to evolve over different phyla and to support different functions. The knowledge of the 3D structure opens the way to the delineation of the mechanism of action of the toxin using site-directed mutagenesis.
- Centre de Biochimie Structurale, UMR 5048 CNRS/UM1-UMR 554 Inserm/UM1, 29 rue de Navacelles, 34090 Montpellier Cedex, France.
Organizational Affiliation: