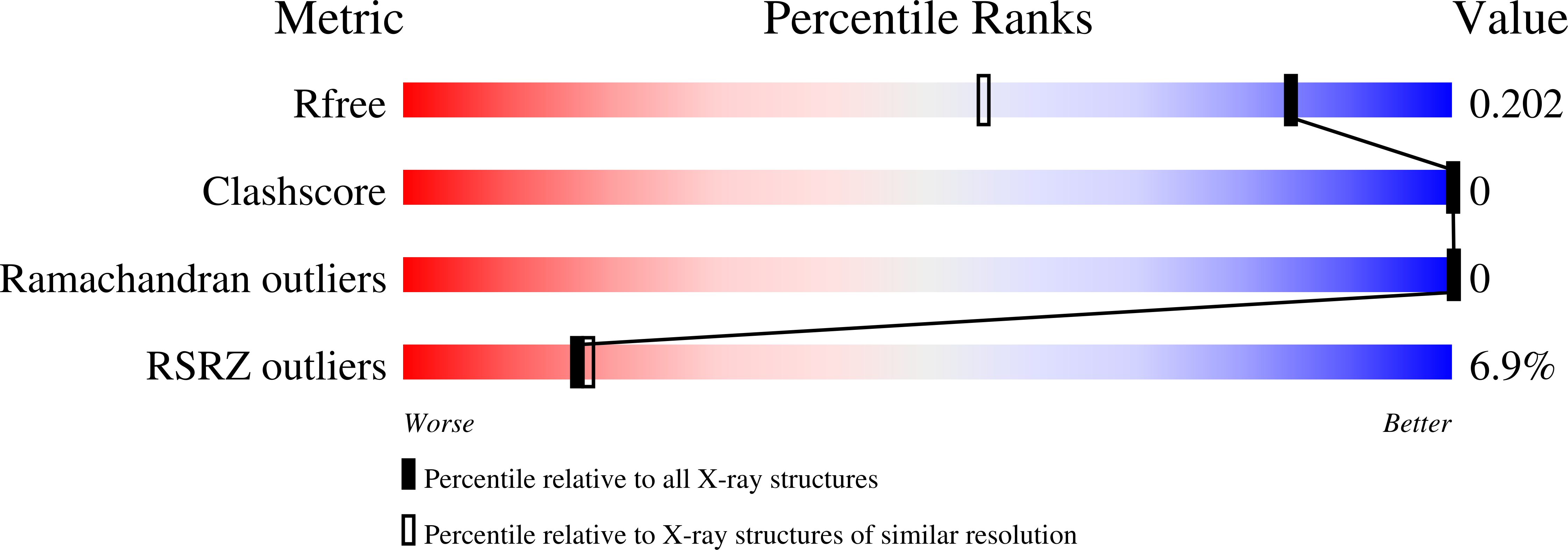Effect of hydration on the stability of the collagen-like triple-helical structure of [4(R)-hydroxyprolyl-4(R)-hydroxyprolylglycine]10
Kawahara, K., Nishi, Y., Nakamura, S., Uchiyama, S., Nishiuchi, Y., Nakazawa, T., Ohkubo, T., Kobayashi, Y.(2005) Biochemistry 44: 15812-15822
- PubMed: 16313184
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi051619m
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WZB - PubMed Abstract:
X-ray analysis has been carried out on a crystal of the collagen model peptide (Hyp(R)-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 [where Hyp(R) is 4(R)-hydroxyproline] with 1.5 A resolution. The triple-helical structure of (Hyp(R)-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 has the same helical parameters and Rich and Crick II hydrogen bond patterns as those of other collagen model peptides. However, our full-length crystal structure revealed that almost all consecutive Hyp(R) residues take the up-up pucker in contrast to putative down-up puckering propensities of other collagen model peptides. The unique feature of thermodynamic parameters associated with the conformational transition of this peptide from triple helix to single coil is that both enthalpy and entropy changes of the transition are much smaller than those of other model peptides such as (Pro-Pro-Gly)10 and (Pro-Hyp(R)-Gly)10. To corroborate the precise structural information including main- and side-chain dihedral angles and intra- and interwater bridge networks, we estimated the degrees of hydration by comparing molecular volumes observed experimentally in solution to those calculated ones from the crystal structure. The results showed that the degree of hydration of (Hyp(R)-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 is comparable to that of (Pro-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 in the triple-helical state, but the former was more highly hydrated than (Pro-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 in the single-coil state. Because hydration reduces the enthalpy due to the formation of a hydrogen bond with a water molecule and diminishes the entropy due to the restriction of water molecules surrounding a peptide molecule, we concluded that the high thermal stability of (Hyp(R)-Hyp(R)-Gly)10 is able to be described by its high hydration in the single-coil state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.