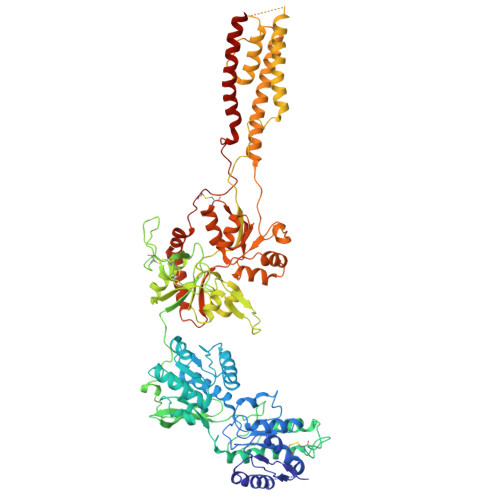
Mechanism of conductance control and neurosteroid binding in NMDA receptors.
Kang, H., Steigerwald, R., Ullman, E.Z., Epstein, M., Paladugu, S., Liotta, D.C., Traynelis, S.F., Furukawa, H.(2025) Nature 648: 220-228
- PubMed: 41162707
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09695-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9OOQ, 9OOR, 9OOS, 9OOT, 9OOU - PubMed Abstract:
Ion-channel activity reflects a combination of open probability and unitary conductance 1 . Many channels display subconductance states that modulate signalling strength 2,3 , yet the structural mechanisms governing conductance levels remain incompletely understood. Here we report that conductance levels are controlled by the bending patterns of pore-forming transmembrane helices in the heterotetrameric neuronal channel GluN1a-2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). Our single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) analyses demonstrate that an endogenous neurosteroid and synthetic positive allosteric modulator (PAM), 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), binds to a juxtamembrane pocket in the GluN2B subunit and stabilizes the fully open-gate conformation, where GluN1a M3 and GluN2B M3' pore-forming helices are bent to dilate the channel pore. By contrast, EU1622-240 binds to the same GluN2B juxtamembrane pocket and a distinct juxtamembrane pocket in GluN1a to stabilize a sub-open state whereby only the GluN2B M3' helix is bent. Consistent with the varying extents of gate opening, the single-channel recordings predominantly show full-conductance and subconductance states in the presence of 24S-HC and EU1622-240, respectively. Another class of neurosteroid, pregnenolone sulfate, engages a similar GluN2B pocket, but two molecules bind simultaneously, revealing a diverse neurosteroid recognition pattern. Our study identifies that the juxtamembrane pockets are critical structural hubs for modulating conductance levels in NMDAR.
- W.M. Keck Structural Biology Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: