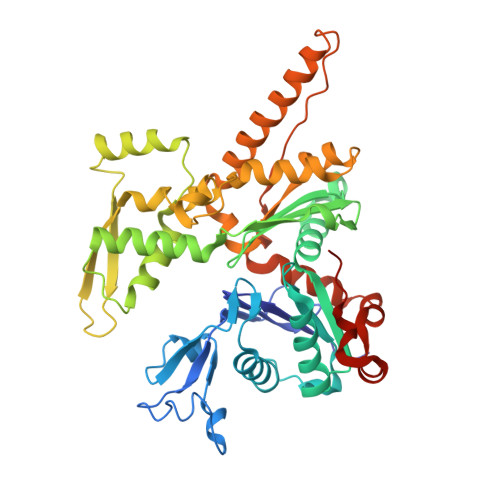
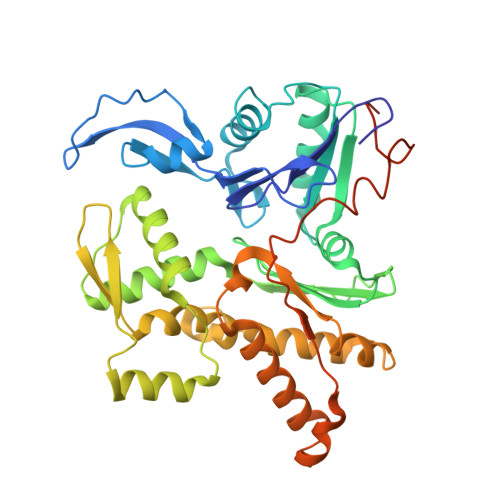
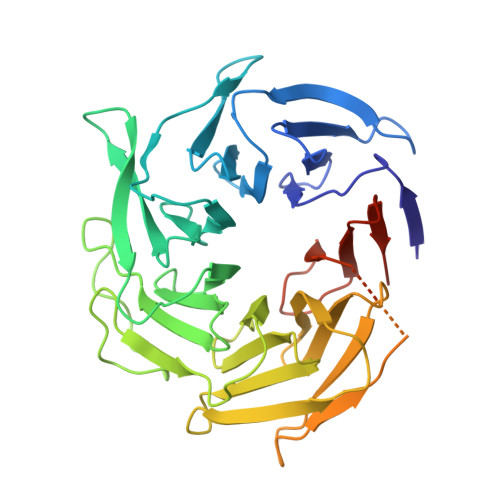
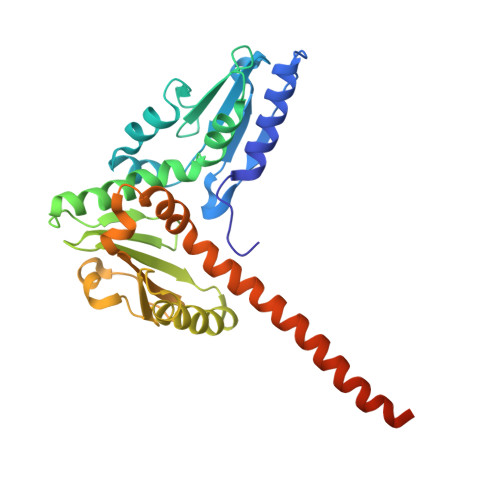
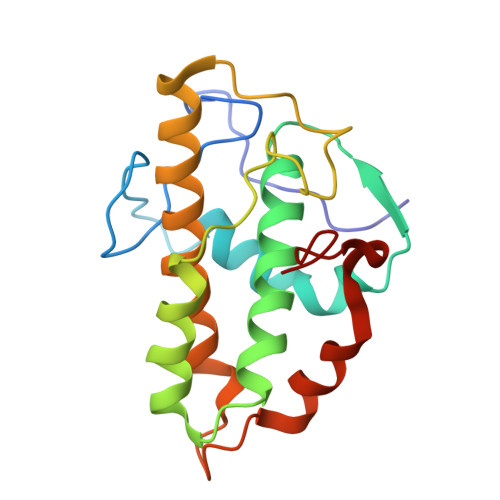
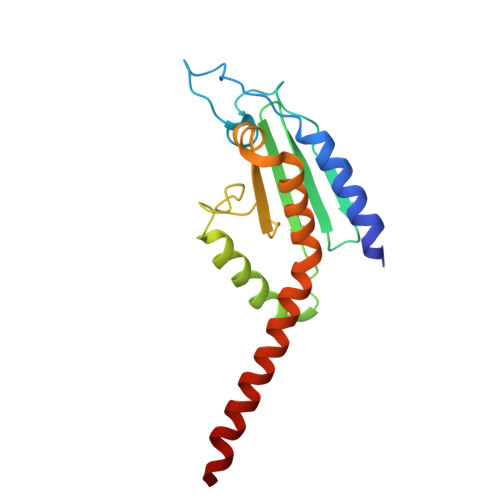
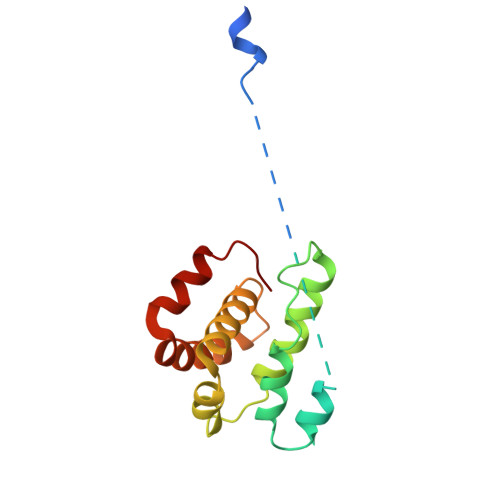
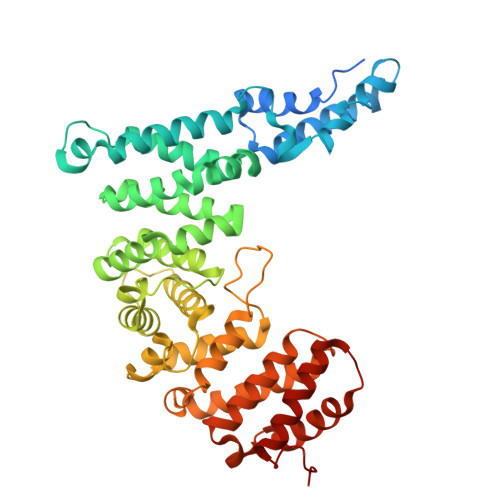
Activation of Arp2/3 complex by a SPIN90 dimer in linear actin-filament nucleation.
Francis, J., Pathri, A.K., Shyam, K.T., Sripada, S., Mitra, R., Narvaez-Ortiz, H.Y., Eliyan, K.V., Nolen, B.J., Chowdhury, S.(2025) Nat Struct Mol Biol 32: 2272-2284
- PubMed: 40954370
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-025-01673-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9M5E, 9M64 - PubMed Abstract:
Arp2/3 complex is a key nucleator of actin filaments. It requires activation by nucleation-promoting factors (NPFs). WISH/DIP1/SPIN90 (WDS) proteins represent a unique class of NPFs that activate the Arp2/3 complex independently of preexisting filaments, promoting linear actin-filament nucleation. In fission yeast, Dip1 binds to the clamp subunits in Arp2/3 complex to induce the short-pitch conformation, where Arp2 moves closer to Arp3 to mimic a filamentous actin dimer. However, how WDS proteins stimulate subunit flattening in Arp subunits, a 'scissor-like' conformational change akin to what is observed in an actin monomer during filament formation, remained unclear. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human SPIN90 bound to activated bovine Arp2/3 complex on an actin filament pointed end. The structures show that SPIN90 dimerizes through a metazoan-specific domain in the middle segment, engaging both the clamp and the Arp3/ARPC3 interface, to drive the activating conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex. Remarkably, a single SPIN90 dimer can also bridge two Arp2/3 complexes, enabling bidirectional actin nucleation and suggesting a mechanism for rapidly assembling complex actin network architectures.
- CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad, India.
Organizational Affiliation: