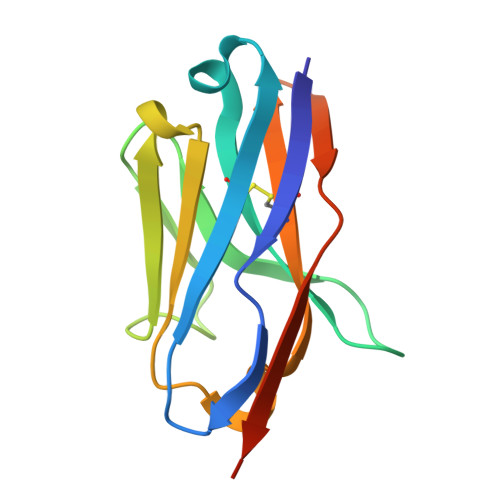
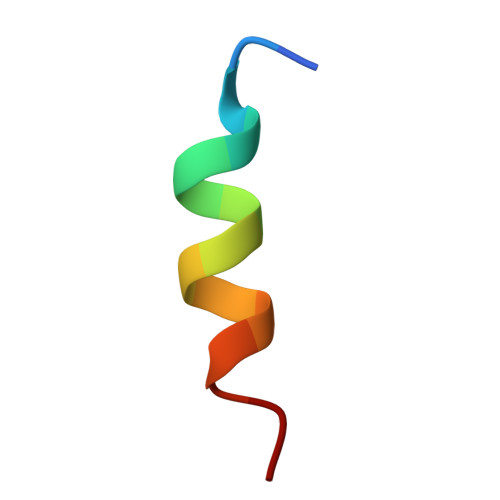
Structural basis and mode of action for two broadly neutralizing nanobodies targeting the highly conserved spike stem-helix of sarbecoviruses including SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Guo, L., Chen, Z., Lin, S., Yang, F., Yang, J., Wang, L., Zhang, X., Yuan, X., He, B., Cao, Y., Li, J., Zhao, Q., Lu, G.(2025) PLoS Pathog 21: e1013034-e1013034
- PubMed: 40215243
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1013034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9LDS - PubMed Abstract:
The persistent emergence of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants highlights the need for developing broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Here, we report the identification of two sarbecovirus S2-specific alpaca nanobodies, namely H17 and H145, that effectively neutralize known SARS-CoV-2 variants (including the Omicron subvariants) and other sarbecoviruses (such as SARS-CoV, PANG/GD, WIV1, and HKU3). The two nanobodies recognize a linear epitope (D1139PLQPELDSFKEEL1152) in the upper region of the S2 stem-helix (SH), which is highly conserved among SARS-CoV-2 variants and other sarbecoviruses. The complex structure of the nanobody bound to the epitope SH-peptide reveal that nanobody binding will impede the refolding of S2, effectively neutralizing the virus. Moreover, the nanobodies bind viral S2 in an acidification-insensitive manner, demonstrating their capacity for entry inhibition especially when viruses enter via the endosomal route. Finally, H17 and H145 possess a better taking-action window for virus neutralization, superior to the RBD-targeting nanobodies that exert neutralization by competing against ACE2 binding. Taken together, the results suggest that anti-SH nanobodies H17 and H145 are promising broad-spectrum drug candidates for preventing and treating the pandemic infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants and other sarbecoviruses.
- Department of Emergency Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Organizational Affiliation: