AlphaFold-guided structural analyses of nucleosome binding proteins.
Yang, X., Zhu, H., Shi, L., Song, T., Gong, W., He, S., Shan, S., Xu, C., Zhou, Z.(2025) Nucleic Acids Res 53
- PubMed: 40794873
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf735
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KQ2 - PubMed Abstract:
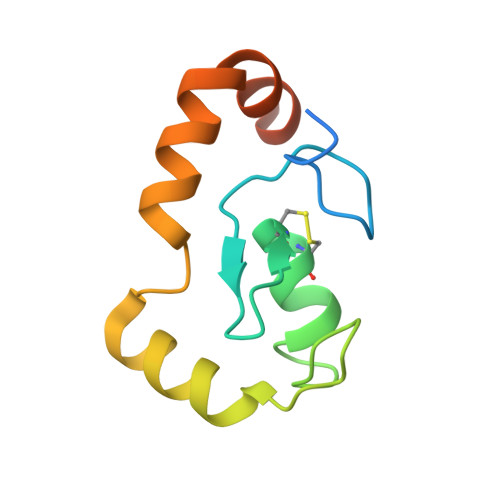
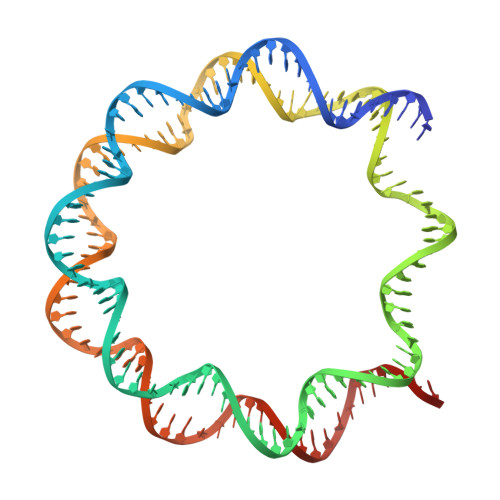
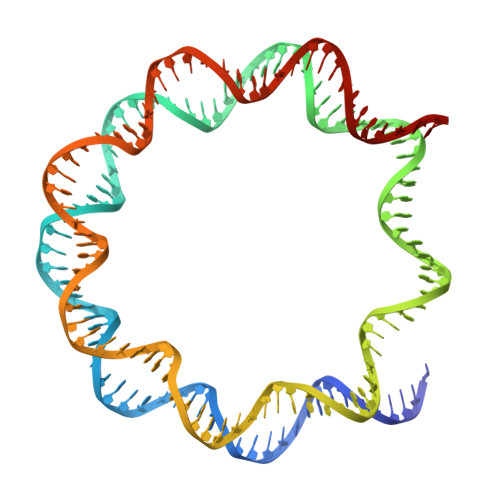
The nucleosome, as the fundamental unit of chromatin, interacts with a diverse range of proteins, crucially regulating gene expression. In this study, we introduce an AlphaFold-based algorithm designed to analyze nucleosome-binding proteins from a dataset of over 7600 human nuclear proteins. Using proteins that interact with the nucleosome acidic patch as a benchmark, our screening achieves a successful prediction rate of 77% (23 out of 30 proteins). This predictive approach has led to the identification of ARID4A and ARID4B as novel nucleosome-binding proteins. Additionally, this analytical method was used to study RING-family ubiquitin E3 ligase RNF168, demonstrating that RNF168 dimerization enhances its binding to the nucleosome, a finding confirmed by cryogenic-electron microscopy structural analysis. Our findings offer a rapid and effective method for the discovery and characterization of nucleosome-binding proteins and emphasize the significant role of ubiquitin E3 ligase dimerization in epigenetic regulation.
- Key Laboratory of Epigenetic Regulation and Intervention, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
Organizational Affiliation: