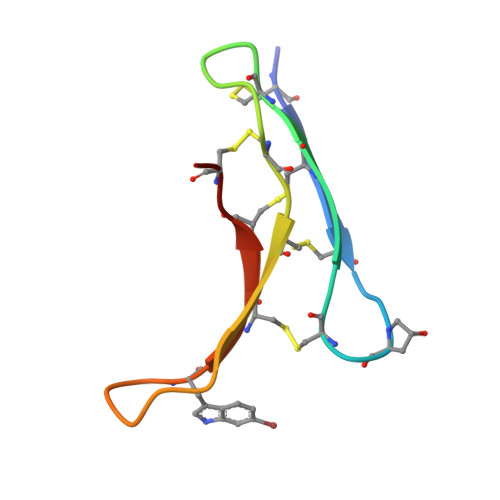
Structural characterisation of a cysteine-rich conotoxin, sigma( sigma )S-GVIIIA, extracted from the defensive venom of the marine cone snail Conus geographus.
Peck, Y., Wilson, D., Lennox-Bulow, D., Giribaldi, J., Seymour, J., Dutertre, S., Rosengren, K., Liddell, M., Daly, N.(2025) Biochem J 482: 639-653
- PubMed: 40272992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20240753
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9EBE - PubMed Abstract:
The activity of the serotonin type 3 (5-HT3) receptor is associated with neurodegenerative, inflammatory and metabolic diseases, neuropsychiatric disorders, and cancer. Structural analysis of modulators of this receptor is likely to aid in future medicinal chemistry studies aimed at developing lead molecules targeting this receptor. Here we report the structure of a cone snail venom peptide that was purified from the crude venom of Conus geographus and shown to be an antagonist of the 5-HT3 receptor more than 25 years ago, sigma(σ)GVIIIA. This lag in structural characterisation studies is likely due to challenges in isolating the native peptide and difficulties in producing synthetic peptide due to the presence of ten cysteine residues involved in five disulfide bonds. Using NMR spectroscopy, we show that σS-GVIIIA adopts a growth factor cystine knot (GFCK) fold. This is the first example of a cone snail venom peptide experimentally determined to contain the GFCK structural motif, and the first example of a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist containing this motif. Our study also highlights complexities in the use of artificial intelligence-based structure prediction models. Peptide structure predictions using AlphaFold 3 were consistent with our NMR structure when the input sequence contained the well-conserved precursor sequence, but inconsistent when the precursor sequence was excluded. AI-based structure prediction of proteins is a rapidly advancing field, but this inconsistency emphasises the need for more experimental structural training data when novel structures are involved, as was the case here for a cysteine-rich peptide.
- Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, James Cook University, Cairns, QLD, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: