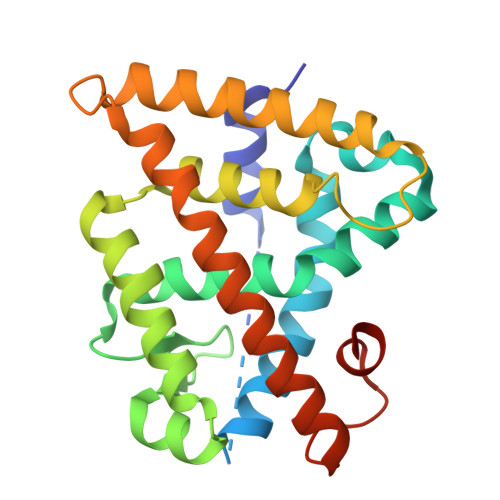
Structural Tuning of Partial RXR Agonism and Antagonism.
Lewandowski, M., Granger-Riviere, M., Mayer, D., Kasch, T., Nawa, F., Egner, M., Marschner, J.A., Morozov, V., Merk, D.(2025) J Med Chem 68: 25255-25273
- PubMed: 41276988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c02270
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9S70, 9S71 - PubMed Abstract:
Retinoid X receptors (RXRs) represent a central switch in nuclear receptor signaling and appear to hold therapeutic potential in diverse indications. However, the ability of RXR agonists to activate multiple nuclear receptor heterodimers gives rise to adverse effects, which may be avoided by partial RXR agonism. In exploring the SAR of a partial agonist scaffold, we identified a region that allowed tuning of RXR activation efficacy between various levels of partial agonism and antagonism. Co-crystal structure analysis revealed dual steric pressure and a combination of reciprocal structural effects to mediate partial agonist activity providing a molecular basis for structural tuning of RXR modulators.
- Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Department of Pharmacy, Munich 81377, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: