DEVELOPMENT OF A POTENT MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY FOR TREATMENT OF HUMAN METAPNEUMOVIRUS INFECTIONS.
Harris, E.D., McGovern, M., Pernikoff, S., Ikeda, R., Kipnis, L., Hannon, W., Sobolik, E.B., Gray, M., Greninger, A.L., He, S., Chin, C.N., Fu, T.M., Pancera, M., Boonyaratanakornkit, J.(2025) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 40666860
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.09.657676
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9ORE - PubMed Abstract:
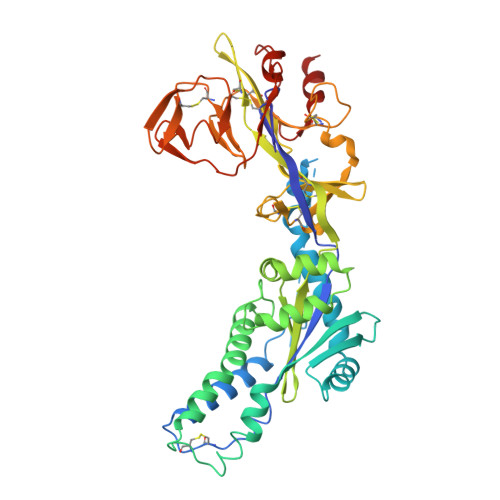
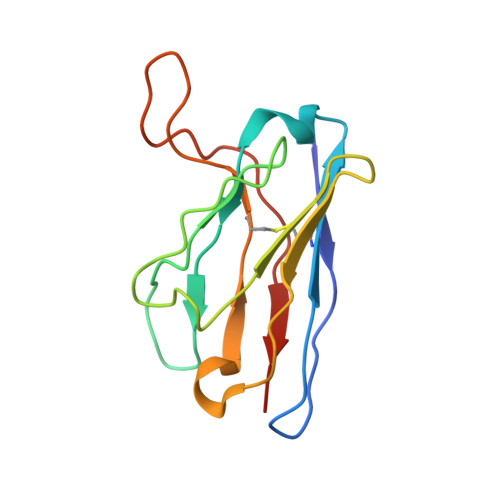
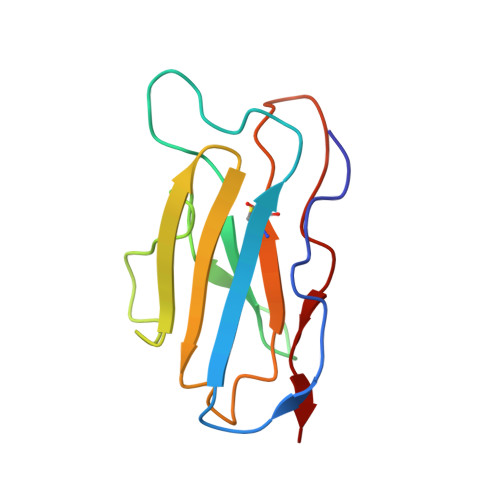
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a major cause of respiratory infections, particularly among vulnerable populations, yet effective therapeutics remain unavailable. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) offer a promising approach for both treatment and prevention. Here, we describe the discovery and characterization of 4F11, a highly potent and broadly neutralizing mAb with demonstrated in vitro and in vivo efficacy against HMPV. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we defined a unique mechanism of binding HMPV employed by 4F11, which distinguishes it from previously characterized RSV and HMPV mAbs. 4F11 targets an epitope located at the apex of the prefusion F protein (site Ø) with a 1:1 stoichiometry, distinct from the 3:1 stoichiometry observed with other HMPV site Ø antibodies. Unlike other site Ø antibodies, which penetrate the glycan shield between Asn57 and Asn172, 4F11 binds vertically and directly interacts with the Asn172 glycan, representing a unique glycan-dependent mode of recognition. In vitro, 4F11 displayed high potency and broad neutralization across diverse HMPV strains. It also showed a low propensity for resistance development, with only a single escape mutation (K179E) identified, a mutation not found in any published HMPV sequence to date. Viruses rescued with the K179E escape mutation had significantly decreased fitness in vitro compared to wild-type virus. In a hamster challenge model, 4F11 significantly reduced viral loads in both the lungs and nasal turbinates. These findings highlight 4F11 as a promising candidate for therapeutic development, particularly for immunocompromised individuals and other high-risk groups.