Structural and Functional Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factor AaaA, an Autotransporter with Arginine-Specific Aminopeptidase Activity.
Arachchige, E.J., Rahman, M.S., Singendonk, K.S., Kim, K.H.(2025) J Mol Biology 437: 169358-169358
- PubMed: 40716734
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169358
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9OQA - PubMed Abstract:
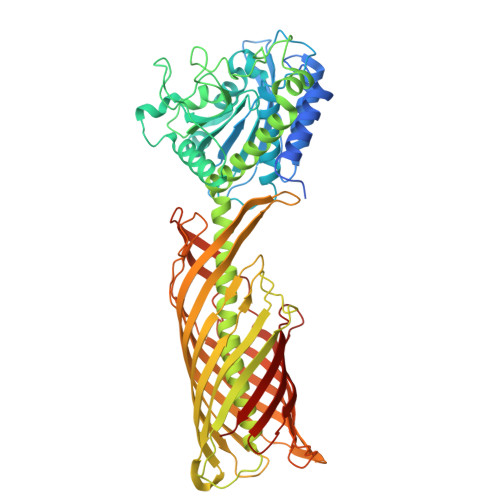
AaaA is a virulence-associated outer membrane protein found in the Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Classified as both an autotransporter and a member of the M28 family of aminopeptidases, AaaA has been shown to cleave N-terminal arginine residues from host-derived peptides. This activity has been demonstrated to enhance bacterial survival and suppress host immune responses by increasing local arginine availability. Here, we report the first successful purification and combined structural and biochemical characterization of full-length AaaA. We resolved its cryo-EM structure at 3.87 Å resolution, revealing the canonical three-domain architecture of autotransporters: a signal peptide, a passenger domain, and a translocator domain. Notably, the passenger domain adopts a compact globular fold characteristic of M28 aminopeptidases, which is less common than the extended or β-helical structures observed in the majority of autotransporters structurally characterized to date. The structure reveals a zinc-coordinated catalytic site and a negatively charged substrate binding pocket, consistent with specificity for positively charged N-terminal arginine residues. Mutagenesis of active site residues confirmed the molecular basis for arginine recognition. Functional assays demonstrated that AaaA exhibits zinc-dependent aminopeptidase activity across a broad pH (6-10) and temperature (20-60 °C) range. Together, these findings provide fundamental insights into the structure and function of AaaA and establish a framework for future efforts to develop targeted inhibitors that may attenuate P. aeruginosa virulence.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: