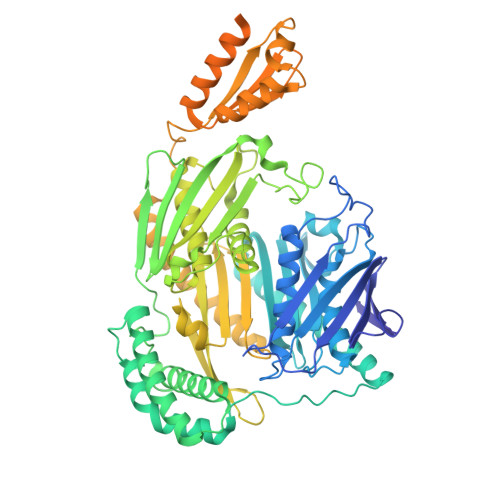
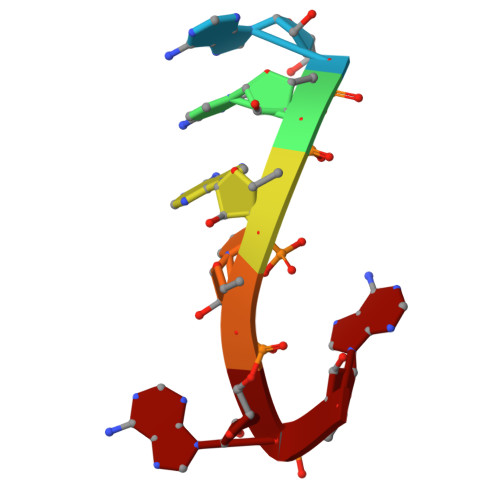
Loop-mediated regulation and base flipping drive RNA cleavage by human mitochondrial PNPase.
Unseld, O., Das, H., Hallberg, B.M.(2025) Nucleic Acids Res 53
- PubMed: 41361968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1296
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9NJB, 9NJC, 9NJD, 9NJE, 9NO0, 9XYI, 9XZF - PubMed Abstract:
Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase), a trimeric exoribonuclease, is crucial for maintaining mitochondrial RNA metabolism, including the regulated degradation of RNA. Mutations in hPNPase have been linked to mitochondrial pathologies, underscoring its importance in mitochondrial RNA homeostasis. Despite this significance, the molecular basis of its catalytic mechanism and the structural consequences of active-site mutations remain poorly understood. We employed high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy to capture three distinct functional states of hPNPase during RNA degradation. In the loading state, flexible loops facilitate the recruitment of the substrate RNA and guide it toward the active site. During the pre-catalytic state, terminal nucleotides reorient within the active site, positioning the RNA backbone for cleavage, which is stabilized by Mg2+. Finally, the catalytic state reveals a nucleophilic attack of phosphate on the RNA backbone, mediated by key active-site residues. These results offer a clear biochemical framework for hPNPase-mediated RNA turnover, clarifying its catalytic mechanism and highlighting how active-site integrity is crucial for efficient RNA degradation.
- Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm 171 77, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: