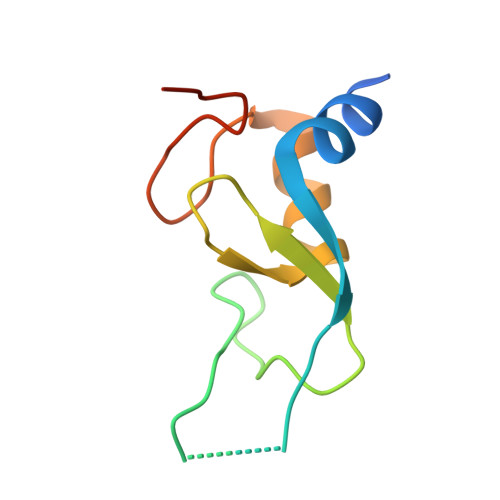
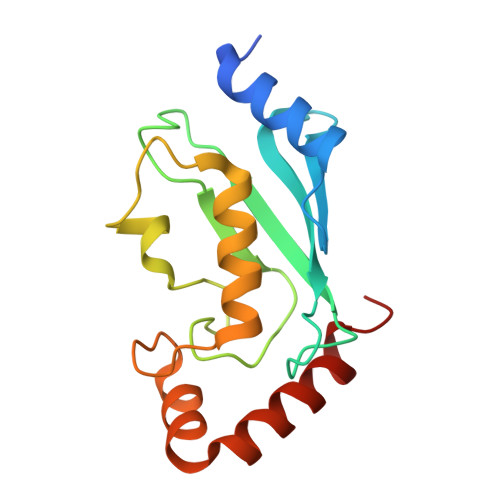
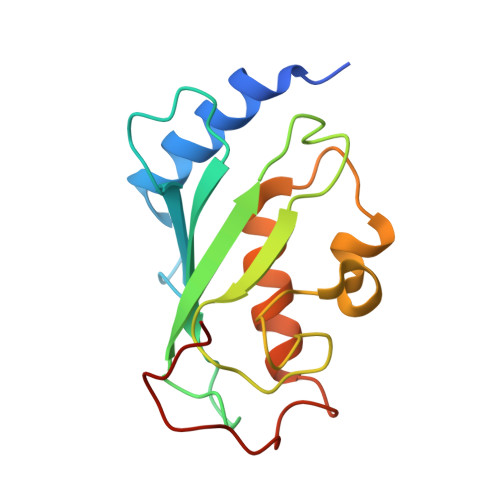
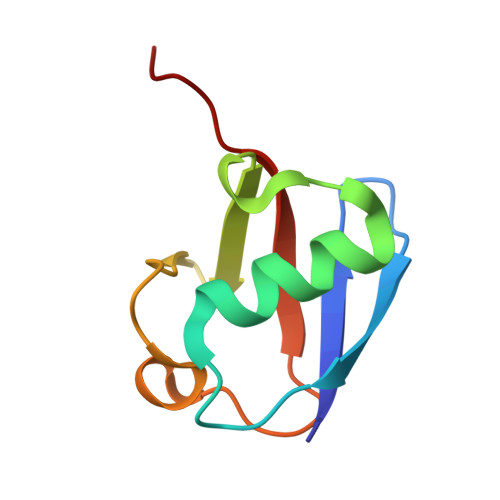
Arkadia and Ark2C Promote Substrate Ubiquitylation with Multiple E2 Enzymes.
Rossig, C., Paluda, A., Chen, R., Middleton, A.J., Day, C.L.(2025) J Mol Biology 437: 169259-169259
- PubMed: 40451499
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169259
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9N1F - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitylation is a critical post-translational modification that is required for cell vitality. Attachment of ubiquitin is complex, with the fate of ubiquitylated proteins determined by the length of the attached ubiquitin chains and the nature of the linkage used to build the chains. Many E3 ligases attach ubiquitin chains of different types to substrate proteins in a context specific manner, but the molecular details of how E3 ligases specify chains of different types is poorly understood. Arkadia/RNF111 is a large RING E3 ligase that modifies some substrates with degradative ubiquitin chains, while other substrates are modified with non-degradative ubiquitin chains. Here, using Arkadia and the related E3 ligase, Ark2C, we characterize the RING-E2 complexes that promote assembly of ubiquitin chains of distinct linkages. Our structural studies highlight the conserved nature of the RING-E2 interface, while our binding and activity assays reveal several different E2 enzymes that functionally interact with Ark2C and Arkadia. Using Arkadia, substrate ubiquitylation assays reveal differences in the ability for substrates to be modified, with the E2 enzymes Ubc13 and Ube2K requiring addition of a 'priming' ubiquitin molecule before subsequent modification can occur. We also show that substrates that bind Arkadia tightly are more extensively modified, and that prior substrate ubiquitylation enhances subsequent modification. While further studies will be required to understand how RING-E2 pairing is modulated in cells, this study advances our understanding of E2 recruitment and chain assembly by Arkadia and provides tools that may help dissect cellular function.
- Biochemistry Department, School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Otago, Dunedin 9054, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: