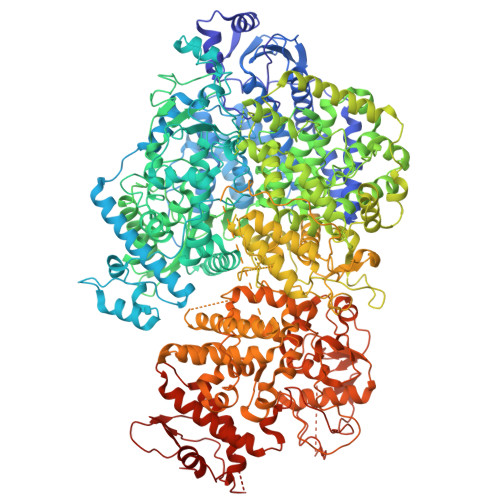
Structural insights into the dynamic mechanism of bornavirus polymerase.
Yang, G., Wang, D., Liu, B.(2025) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 122: e2504779122-e2504779122
- PubMed: 40996804
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2504779122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9N0Q, 9N0R, 9N0S, 9N0T, 9N0U - PubMed Abstract:
Borna disease virus 1 (BoDV-1), an emerging zoonotic pathogen from the Bornaviridae family, is neurotropic and can infect a variety of mammalian hosts, including humans. Linked to severe encephalitis and high mortality, BoDV-1 currently lacks licensed treatments or vaccines. The BoDV-1 polymerase complex, comprising the large (L) and phosphoprotein (P) subunits, is crucial for viral replication and transcription, making it a promising target for antiviral intervention. Here, we present the cryoelectron microscopy structure of the apo BoDV-1 L-P complex, revealing a unique "mitten-shaped" architecture. The structure characterizes key domains involved in RNA synthesis, including RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, polyribonucleotidyltransferase, and an inactive methyltransferase domain. While no RNA or NTPs were visible, we observed distinct conformational states, showing large-scale rearrangements of the P tetramer and L domains, as well as remodeling of the RNA template, nucleoside triphosphates, and nascent RNA entrances and/or exits, upon introducing RNA and NTPs. These findings highlight the dynamic structural changes probably associated with polymerase activity and advance the understanding of the BoDV-1 polymerase mechanisms, offering a basis for developing targeted antiviral strategies against this deadly pathogen.
- Section of Transcription & Gene Regulation, The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, MN 55912.
Organizational Affiliation: