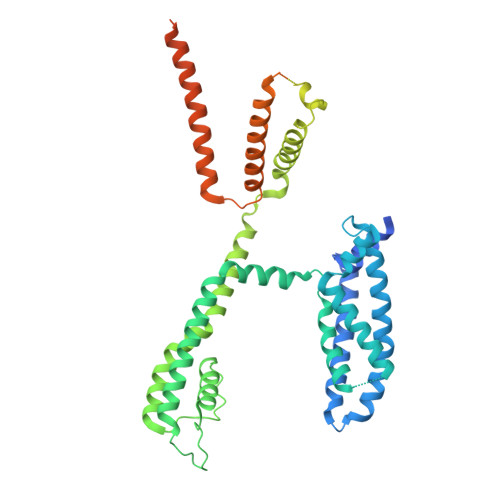
A physiologically-relevant intermediate state structure of a voltage-gated potassium channel.
Kyriakis, E., Sastre, D., Eldstrom, J., Roscioni, A., Russo, S., Ataei, F., Dou, Y., Chan, M., Molinarolo, S., Maragliano, L., Van Petegem, F., Fedida, D.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 8814-8814
- PubMed: 41044058
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64060-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9MY3, 9MY4 - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated potassium ion (K + ) channels perform critical roles in many physiological processes, while gain- or loss-of-function mutations lead to life-threatening pathologies. Here, we establish the high-resolution structure of a pivotal intermediate state of the Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) channel using cryogenic electron microscopy. The 3.53 Å resolution structure reveals straightened upper S1 and S2 voltage sensor helices, distancing them from the pore filter helix compared to fully activated channels. The outward translation of the S4 voltage sensor is essentially complete in this intermediate state, and the S4-S6 helices and the S4-S5 linker do not change position significantly between intermediate and activated states. The PIP2 ligand can bind in both states. Movement of S1 and S2 helices towards the filter helix from intermediate to activated states may explain smaller components of KCNQ1 voltage sensor fluorescence, differential Rb + /K + selectivity, and pharmacological responses to activators and inhibitors. Single channel recordings and the location of long QT mutations suggest the potential physiological and disease importance of the intermediate state.
- The Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, V6T 1Z3, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: