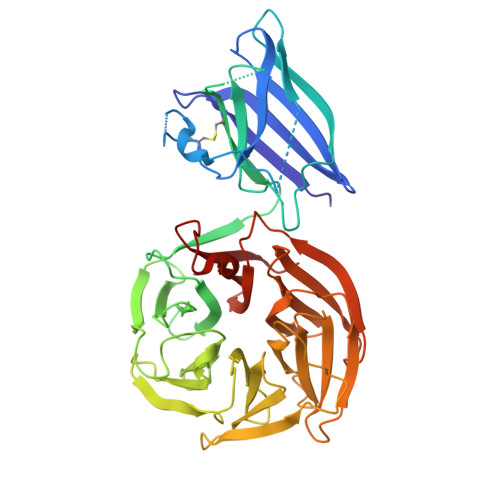
Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase naturally fused with a beta-propeller lactonase in Deinococcus radiodurans.
Furukawa, Y., Megata, M., Shintani, A., Sue, K., Morohoshi, T., Akutsu, M., Muraki, N.(2025) J Biological Chem 301: 110499-110499
- PubMed: 40684944
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110499
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9M58, 9M59 - PubMed Abstract:
Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD) is an antioxidant enzyme widely present across species; however, the structural diversity and physiological roles of Cu/Zn-SOD are yet to be fully uncovered. Here, we show a unique type of Cu/Zn-SOD from Deinococcus radiodurans (DrSOD) with an additional β-propeller domain. Our structural analysis of DrSOD revealed a typical bacterial Cu/Zn-SOD domain, binding both a copper and zinc ion, alongside a six-bladed β-propeller domain coordinating a calcium ion. DrSOD was indeed expressed in D. radiodurans, but its deletion did not lead to any noticeable changes in resistance to DNA-damaging stresses, a characteristic trait of D. radiodurans. Despite this, the Cu/Zn-SOD domain retained superoxide dismutase activity, and the β-propeller domain was found to exhibit a lactonase activity specifically for hydrolyzing 2-coumaranone. Taken together, while the precise physiological role of DrSOD needs to be further investigated, our findings here reveal a unique multi-functional enzyme architecture, expanding the known structural diversity of Cu/Zn-SODs.
- Department of Chemistry, Keio University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan. Electronic address: furukawa.a3@keio.jp.
Organizational Affiliation: