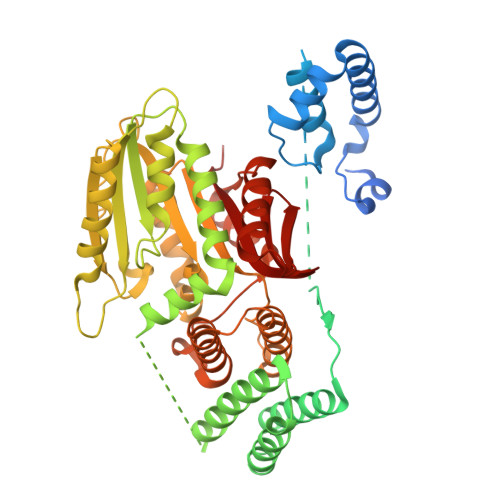
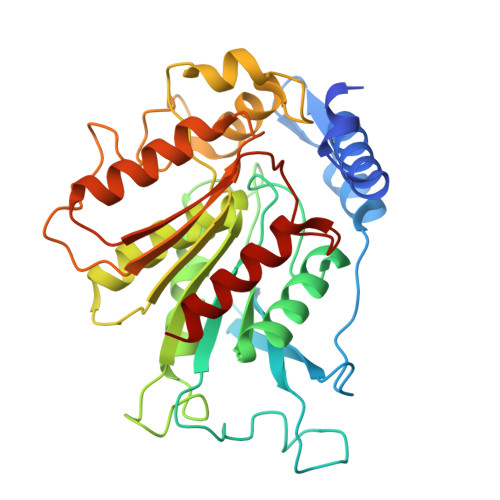
Structural insights into gibberellin-mediated DELLA protein degradation.
Islam, S., Park, K., Xia, J., Kwon, E., Kim, D.Y.(2025) Mol Plant 18: 1210-1221
- PubMed: 40542507
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2025.06.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9LUM, 9LUN, 9LUO, 9LUP - PubMed Abstract:
Gibberellin promotes plant growth by downregulating DELLA proteins, which act as growth repressors. In the presence of gibberellin, the gibberellin receptor GID1 binds DELLA proteins, triggering their degradation through polyubiquitination by the SCF SLY1/GID2 ubiquitin E3 ligase. Despite extensive studies, the molecular mechanisms by which DELLA proteins assemble with SCF SLY1/GID2 to regulate plant growth remain poorly understood. Here, we present two cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Arabidopsis thaliana DELLA protein RGA in complex with GID1A and GID1A-SLY1-ASK2, respectively. Structural analyses revealed that RGA interacts with GID1A and SLY1 through nonoverlapping binding surfaces, stabilizing the proteins. This suggests that the SCF SLY1 -RGA-GID1A complex assembles through a stepwise stabilization process induced by gibberellin. Furthermore, structural comparison with GRAS proteins indicates that RGA does not interact with IDD-family transcription factors when bound to SLY1, suggesting that DELLA protein binding to GID1/SLY1 and to transcription factors is mutually exclusive. These findings provide new insights into the gibberellin-mediated regulation of transcription factor activity by DELLA proteins.
- College of Pharmacy, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan 38541, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: