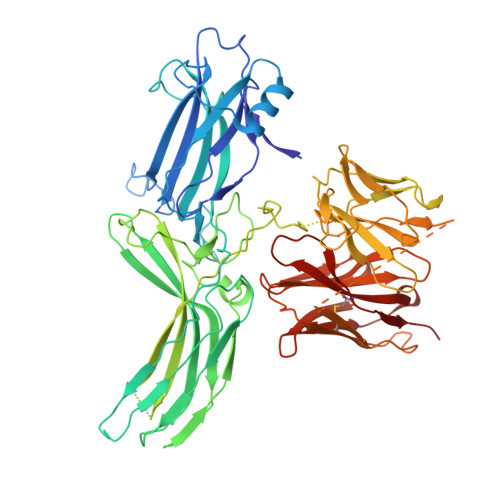
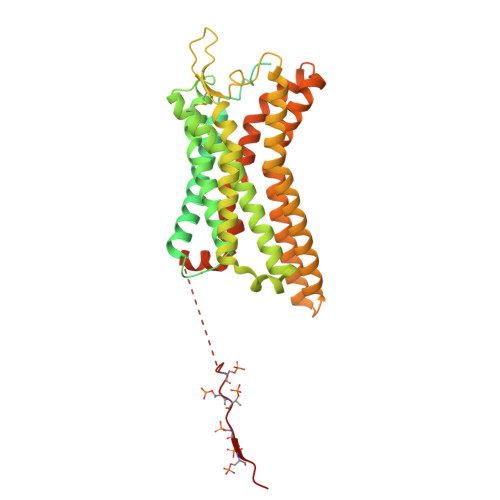
Mechanistic insights into the versatile stoichiometry and biased signaling of the apelin receptor-arrestin complex.
Yue, Y., Xu, C., Wu, L., Na, M., Xu, K., Chen, X., Song, Y., Weng, S., Xu, L., Li, F., Lin, X., Wang, A., Liu, J., Xu, F.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 7403-7403
- PubMed: 40790299
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62870-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KUV, 9KUW, 9KUX - PubMed Abstract:
The apelin receptor (APJR) plays a pivotal role in regulating cardiovascular and metabolic health 1,2 . Understanding the mechanisms of biased agonism at APJR is crucial for drug discovery, as stimulation of the β-arrestin pathway may lead to some adverse effects 3 . Structural analyses of APJR-Gi complexes have clarified the structural basis of receptor dimerization and activation 4,5 , yet the absence of structural data on APJR-arrestin complexes has impeded a comprehensive understanding of APJR stoichiometry in the dual signaling pathways and biased agonism. Here, we present APJR-β-arrestin1 structures bound to a clinical drug analog, revealing 2:2 and 2:1 stoichiometries associated with differential β-arrestin recruitment. Through comparison of the two transducer-coupled APJR structures bound to the same ligand, we identify key residues and motifs crucial for directing biased signaling. These findings highlight APJR's versatile stoichiometry in coupling with β-arrestin and Gi proteins, establishing a framework for understanding biased agonism and guiding the development of therapeutics.
- iHuman Institute, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: