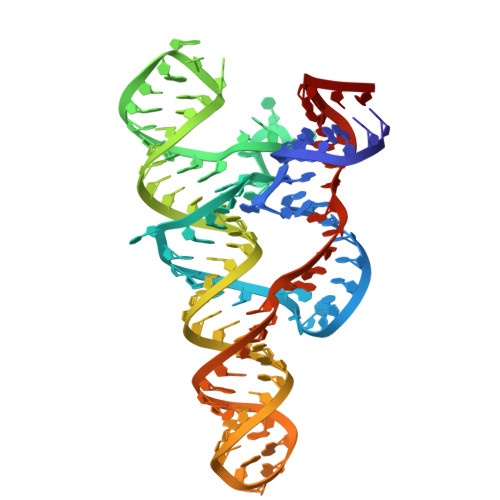
Escherichia coli yybP-ykoY Riboswitch as a Tandem Riboswitch Regulated by Mn 2+ and pH.
Xiao, W., Liu, G., Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Ke, A., Cai, R., Lu, C.(2025) ACS Chem Biol 20: 1010-1019
- PubMed: 40252020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.4c00715
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9JGM - PubMed Abstract:
The Escherichia coli yybP-ykoY riboswitch regulates mntP and alx gene expression on the translation level. It contains two tandem domains regulated by Mn 2+ and pH. This study investigates the tertiary structure and conformational dynamics of the E. coli yybP-ykoY riboswitch using a combination of crystallography, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and chemical probing. Our crystal structure of the aptamer domain at 3.8 Å reveals that the yybP-ykoY riboswitch aptamer domain forms a coaxial superhelix containing three helices connected by a three-way junction (3WJ), with L1 and L3 creating a pocket-like structure that binds Mg 2+ and Mn 2+ . SHAPE probing and SAXS show that the yybP-ykoY riboswitch maintains a consistent conformation across pH conditions without Mn 2+ but exhibits significant conformational changes under alkaline conditions when Mn 2+ is present. These findings align with our proposed model, where Mn 2+ binding induces a transition from an "OFF" to an "ON" state in alkaline conditions, while the Mn 2+ remains bound to the aptamer independent of pH. This regulatory mechanism allows for more sophisticated control of gene expression, providing a finely tuned adaptive response to environmental changes.
- College of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China.
Organizational Affiliation: