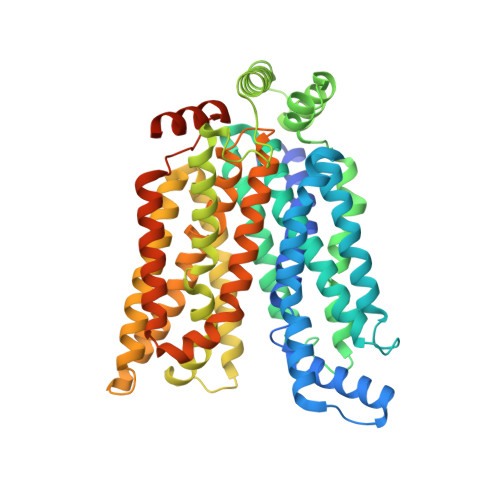
Cryo-EM structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT7.
Lee, S.S., Kim, S., Jin, M.S.(2024) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 738: 150544-150544
- PubMed: 39163817
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150544
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9J2N - PubMed Abstract:
GLUT7 is a Class II glucose transporter predominantly expressed at the apical membrane of enterocytes in the small intestine. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of nanodisc-reconstituted human GLUT7 in the apo state at 3.3 Å resolution. Our atomic model reveals a typical major facilitator superfamily fold, with the substrate-binding site open to the extracellular side of the membrane. Despite the nearly identical conformation to its closest family member, rat GLUT5, our structure unveils distinct features of the substrate-binding cavity that may influence substrate specificity and binding mode. A homology model of the inward-open human GLUT7 indicates that similar to other members of the GLUT family, it may undergo a global rocker-switch-like reorientation of the transmembrane bundles to facilitate substrate translocation across the membrane. Our work enhances the current structural understanding of the GLUT family, and lays a foundation for rational design of regulators of GLUTs and other sugar transporters.
- School of Life Sciences, GIST, 123 Cheomdangwagi-ro, Buk-gu, Gwangju, 61005, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: