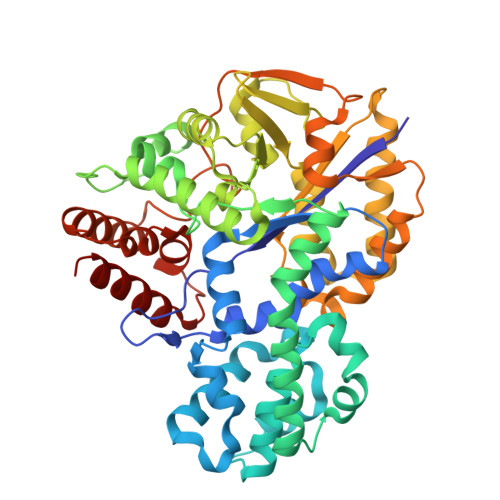
The crystal structure of GH57 family amylopullulanase reveals its dual binding pockets sharing the same catalytic dyad.
Zhu, Z., Wang, W., Li, M., Xu, Q., Zhou, H., Huang, L., Wang, Q., Yu, F.(2025) Commun Biol 8: 806-806
- PubMed: 40419759
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-08192-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ZYI, 9IHT, 9IHU, 9IHV, 9IHW, 9IHX, 9II0, 9II1, 9K7C, 9K7D - PubMed Abstract:
Glycoside Hydrolase Family 57 (GH57) amylopullulanase is a thermophilic endoamylase capable of hydrolyzing both α-1,4 and α-1,6-glycosidic bonds, demonstrating significant potential for one-step starch saccharification in industrial applications. However, the mechanisms underlying the dual catalytic activities of GH57 family amylopullulanase remain poorly understood. In this study, we report the first crystal structures of a GH57 amylopullulanase from Aquifex aeolicus (AaApu) in complex with oligosaccharides containing both α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds. Our structural analysis reveals that GH57 amylopullulanase features dual binding pockets arranged in a "Y"-shaped configuration, which accommodates branched-chain starches. The dual binding pockets share a common catalytic dyad composed of Glu256 and Asp352. Notably, unlike the typical retaining mechanism observed in many glycoside hydrolases, the distance between the catalytic residues in GH57 amylopullulanase is significantly larger (approximately 7 Å). This study provides critical insights into the structural basis of GH57 amylopullulanase activity and offers a foundation for the rational engineering of these enzymes for industrial applications.
- Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: