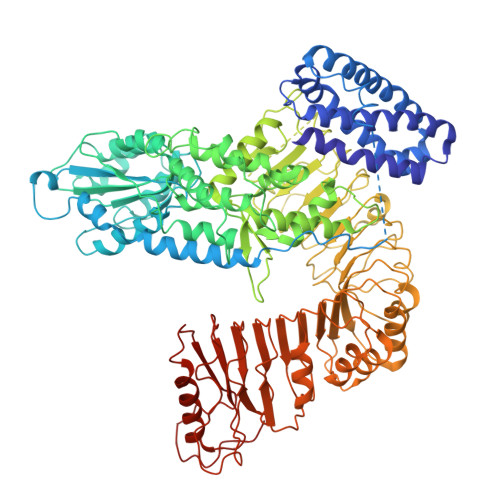
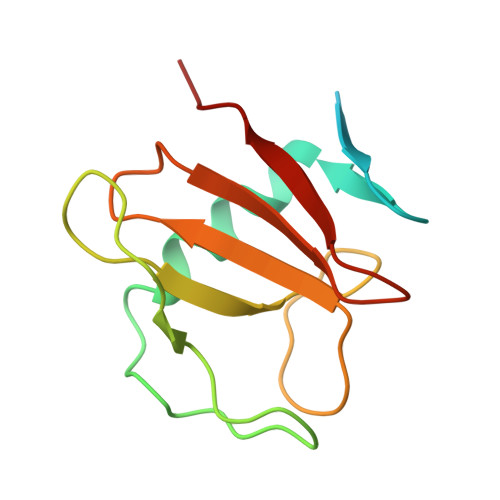
The barley MLA13-AVR A13 heterodimer reveals principles for immunoreceptor recognition of RNase-like powdery mildew effectors.
Lawson, A.W., Flores-Ibarra, A., Cao, Y., An, C., Neumann, U., Gunkel, M., Saur, I.M.L., Chai, J., Behrmann, E., Schulze-Lefert, P.(2025) EMBO J 44: 3210-3230
- PubMed: 39948409
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-025-00373-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9FYC - PubMed Abstract:
Co-evolution between cereals and pathogenic grass powdery mildew fungi is exemplified by sequence diversification of an allelic series of barley resistance genes encoding Mildew Locus A (MLA) nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) immunoreceptors with an N-terminal coiled-coil domain (CNLs). Each immunoreceptor recognises a matching, strain-specific powdery mildew effector encoded by an avirulence gene (AVR a ). We present here the cryo-EM structure of barley MLA13 in complex with its cognate effector AVR A13 -1. The effector adopts an RNase-like fold when bound to MLA13 in planta, similar to crystal structures of other RNase-like AVR A effectors unbound to receptors. AVR A13 -1 interacts via its basal loops with MLA13 C-terminal leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) and the central winged helix domain (WHD). Co-expression of structure-guided MLA13 and AVR A13 -1 substitution variants show that the receptor-effector interface plays an essential role in mediating immunity-associated plant cell death. Furthermore, by combining structural information from the MLA13-AVR A13 -1 heterocomplex with sequence alignments of other MLA receptors, we engineered a single amino acid substitution in MLA7 that enables expanded effector detection of AVR A13 -1 and the virulent variant AVR A13 -V2. In contrast to the pentameric conformation of previously reported effector-activated CNL resistosomes, MLA13 was purified and resolved as a stable heterodimer from an in planta expression system. Our study suggests a common structural principle for RNase-like effector binding to MLAs and highlights the utility of structure-guided engineering of plant immune receptors for broadening their pathogen effector recognition capabilities.
- Department of Plant Microbe Interactions, Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research, 50829, Cologne, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: