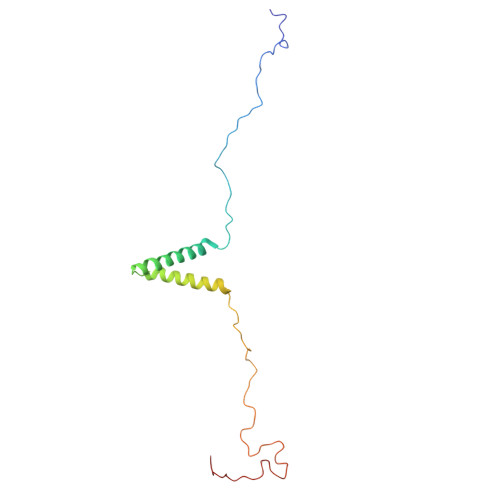
Structure and nucleic acid interactions of the S Delta 60 domain of the hepatitis delta virus small antigen.
Yang, Y., Delcourte, L., van Belleghem, C., Fonte, S., Gerard, K., Baconnais, S., Callon, M., Le Cam, E., Fogeron, M.L., Levrero, M., Faivre-Moskalenko, C., Bockmann, A., Lecoq, L.(2025) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 122: e2411890122-e2411890122
- PubMed: 40324079
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2411890122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9FLG - PubMed Abstract:
Infection with hepatitis delta virus (HDV) causes the most severe form of viral hepatitis, affecting more than 15 million people worldwide. HDV is a small RNA satellite virus of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that relies on the HBV envelope for viral particle assembly. The only specific HDV component is the ribonucleoprotein (RNP), which consists of viral RNA (vRNA) associated with the small (S) and large (L) delta antigens (HDAg). While the structure of the HDAg N-terminal assembly domain is known, here we address the structure of the remaining S Δ60 protein using NMR. We show that S Δ60 contains two intrinsically disordered regions separated by a helix-loop-helix motif and that this structure is conserved in the full-length protein. Solution NMR analysis revealed that S Δ60 binds to both full-length and truncated vRNA, highlighting the role of the helical regions in submicromolar affinity interactions. The resulting complex contains approximately 120 S Δ60 proteins per RNA. Our results provide a model for the arginine-rich domains in RNP assembly and RNA interactions. In addition, we show that a cluster of acidic residues within the structured region of S Δ60 is critical for HDV replication, possibly mimicking the nucleosome acidic patch involved in the recruitment of chromatin remodelers. Our work thus provides the molecular basis for understanding the role of the C-terminal RNA-binding domain of S-HDAg in HDV infection.
- Molecular Microbiology and Structural Biochemistry UMR 5086 CNRS/Université de Lyon, Labex Ecofect, Lyon 69367, France.
Organizational Affiliation: