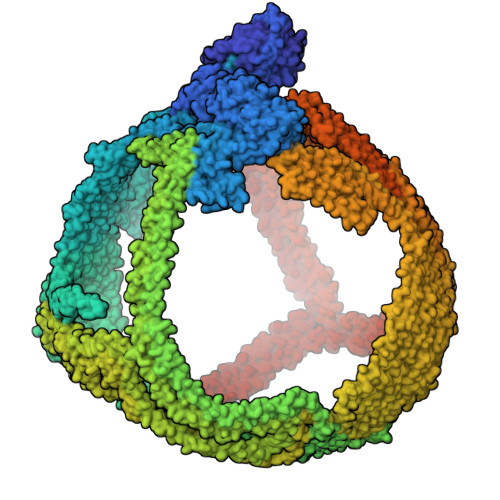
The structure of apolipoprotein B100 from human low-density lipoprotein.
Berndsen, Z.T., Cassidy, C.K.(2025) Nature 638: 836-843
- PubMed: 39662503
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08467-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9E9R, 9EA7, 9EAG - PubMed Abstract:
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) plays a central role in lipid and cholesterol metabolism and is a key agent in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, the leading cause of mortality worldwide 1,2 . Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100), one of the largest proteins in the genome, is the primary structural and functional component of LDL, yet its size and complex lipid associations have posed major challenges for structural studies 3 . Here we present the first structure of apoB100 resolved to sub-nanometer resolution in most regions using an integrative approach of cryo-electron microscopy, AlphaFold2 4 , and molecular dynamics-based refinement 5 . The structure consists of a large globular N-terminal domain and a ~61 nm long continuous amphipathic β-sheet that wraps around the LDL particle like a belt. Distributed quasi-symmetrically across the two sides of the "β-belt" are 9 strategically located inter-strand inserts that extend across the lipid surface to provide additional structural support through a network of long-range interactions. We further compare our structure to a comprehensive list of >200 intramolecular crosslinks and find close agreement between the two. These results suggest a mechanism for how the various domains of apoB100 act in concert to maintain LDL shape and cohesion across a range of particle sizes. More generally, they advance our fundamental understanding of LDL synthesis, form and function and will help accelerate the design of potential new therapeutics.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, USA. zberndsen@missouri.edu.
Organizational Affiliation: