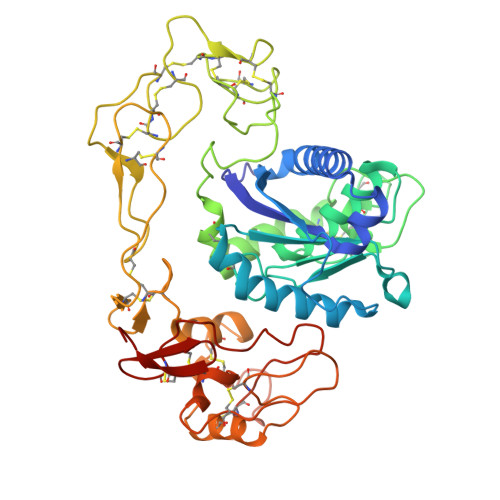
Importance of the Cysteine-Rich Domain of Snake Venom Prothrombin Activators: Insights Gained from Synthetic Neutralizing Antibodies.
Misson Mindrebo, L.E., Mindrebo, J.T., Tran, Q., Wilkinson, M.C., Smith, J.M., Verma, M., Casewell, N.R., Lander, G.C., Jardine, J.G.(2024) Toxins (Basel) 16
- PubMed: 39195771
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16080361
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9CLP - PubMed Abstract:
Snake venoms are cocktails of biologically active molecules that have evolved to immobilize prey, but can also induce a severe pathology in humans that are bitten. While animal-derived polyclonal antivenoms are the primary treatment for snakebites, they often have limitations in efficacy and can cause severe adverse side effects. Building on recent efforts to develop improved antivenoms, notably through monoclonal antibodies, requires a comprehensive understanding of venom toxins. Among these toxins, snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs) play a pivotal role, particularly in viper envenomation, causing tissue damage, hemorrhage and coagulation disruption. One of the current challenges in the development of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against SVMPs is the large size of the protein and the lack of existing knowledge of neutralizing epitopes. Here, we screened a synthetic human antibody library to isolate monoclonal antibodies against an SVMP from saw-scaled viper (genus Echis ) venom. Upon characterization, several antibodies were identified that effectively blocked SVMP-mediated prothrombin activation. Cryo-electron microscopy revealed the structural basis of antibody-mediated neutralization, pinpointing the non-catalytic cysteine-rich domain of SVMPs as a crucial target. These findings emphasize the importance of understanding the molecular mechanisms of SVMPs to counter their toxic effects, thus advancing the development of more effective antivenoms.
- Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: