Structure and activation of the human autophagy-initiating ULK1C:PI3KC3-C1 supercomplex.
Chen, M., Nguyen, T.N., Ren, X., Khuu, G., Cook, A.S.I., Zhao, Y., Yildiz, A., Lazarou, M., Hurley, J.H.(2025) Nat Struct Mol Biol 32: 1596-1605
- PubMed: 40442316
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-025-01557-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9C82 - PubMed Abstract:
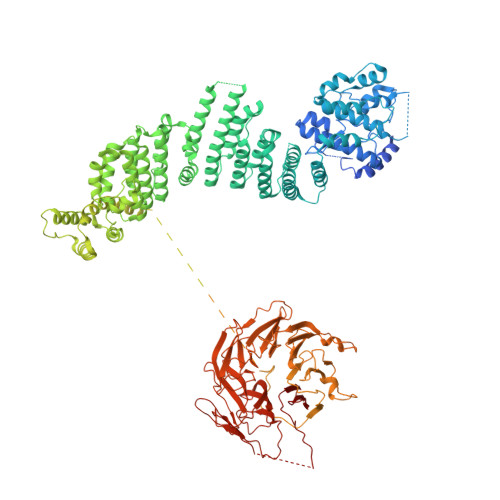
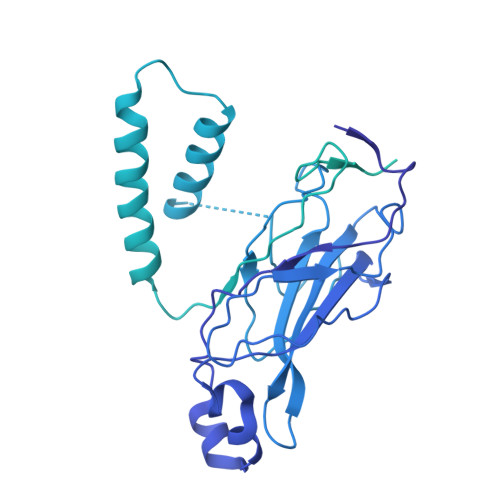
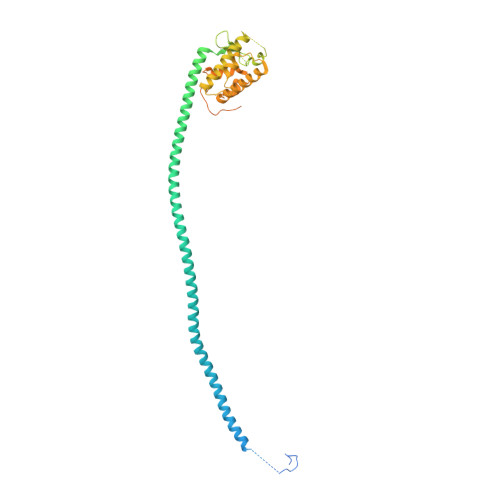
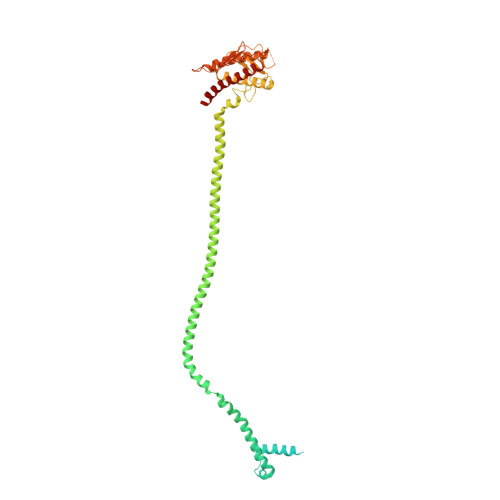
The Unc-51-like kinase protein kinase complex (ULK1C) is the most upstream and central player in the initiation of macroautophagy in mammals. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human ULK1C core at amino-acid-level resolution. We also determined a moderate-resolution structure of the ULK1C core in complex with another autophagy core complex, the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase complex I (PI3KC3-C1). We show that the two complexes coassemble through extensive contacts between the FIP200 scaffold subunit of ULK1C and the VPS15, ATG14 and BECN1 subunits of PI3KC3-C1. The FIP200:ATG13:ULK1 core of ULK1C undergoes a rearrangement from 2:1:1 to 2:2:2 stoichiometry in the presence of PI3KC3-C1. This suggests a structural mechanism for the initiation of autophagy through formation of a ULK1C:PI3KC3-C1 supercomplex and dimerization of ULK1 on the FIP200 scaffold.
- Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: