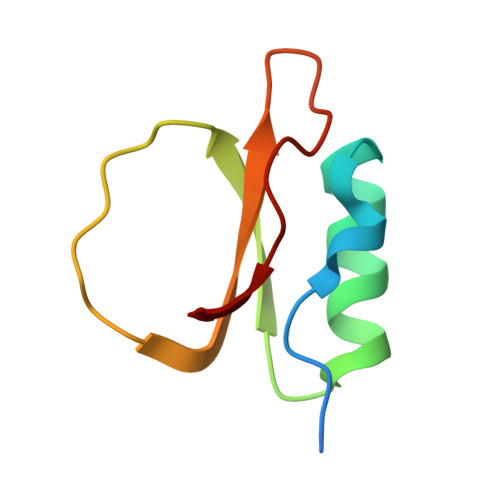
Understanding the structure and function of HPI, a rubber tree serine protease inhibitor, and its interaction with subtilisin.
Terron-Hernandez, J., Gomez-Velasco, H., Pinzon-Yaya, L., Hernandez-Santoyo, A., Garcia-Ramirez, B., Rodriguez-Romero, A.(2025) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 763: 151801-151801
- PubMed: 40233429
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151801
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BLJ - PubMed Abstract:
Protease inhibitors are crucial in regulating enzymatic activity and have extensive applications in medicine, biotechnology, and agriculture. This study characterizes a recombinant protease inhibitor from Hevea brasiliensis (rHPI), highlighting its unique structural features and inhibitory potential. Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization (MALDI) analysis, the inhibitor exhibits one distinct peak around 7.54 kDa. Enzymatic assays using N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide as a substrate confirmed the inhibitor's activity against subtilisin Carlsberg, a widely utilized serine protease in industry and biotechnology. The crystal structure of rHPI, resolved at 1.73 Å, reveals a topology closely resembling eglin c, including a single alpha-helix, two parallel beta-strands, and a distinctive binding loop spanning residues 40-51. Disordered regions at the N- and C-termini contribute to its structural uniqueness. Despite lacking disulfide bonds and featuring an Arg residue instead of Trp at the P' 8 position, rHPI maintains a high affinity for subtilisin. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) showed that this interaction is entropically driven. Molecular docking and dynamics simulations of the rHPI-subtilisin complex revealed the formation of antiparallel β-sheets, hydrogen bonding involving the protein backbone, and a salt bridge between His64 of subtilisin and Asp47 of rHPI. These findings provide valuable insights into the molecular basis of rHPI's inhibitory activity and offer a framework for the rational design of novel subtilisin inhibitors with potential applications in agricultural and industrial settings.
- Instituto de Química, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Circuito Ext. s/n. Ciudad de México 04510, Mexico.
Organizational Affiliation: