A multidonor class of highly glycan-dependent HIV-1 gp120-gp41 interface-targeting broadly neutralizing antibodies.
Cale, E.M., Shen, C.H., Olia, A.S., Radakovich, N.A., Rawi, R., Yang, Y., Ambrozak, D.R., Bennici, A.K., Chuang, G.Y., Crooks, E.D., Driscoll, J.I., Lin, B.C., Louder, M.K., Madden, P.J., Messina, M.A., Osawa, K., Stewart-Jones, G.B.E., Verardi, R., Vrakas, Z., Xie, D., Zhang, B., Binley, J.M., Connors, M., Koup, R.A., Pierson, T.C., Doria-Rose, N.A., Kwong, P.D., Mascola, J.R., Gorman, J.(2024) Cell Rep 43: 115010-115010
- PubMed: 39675002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BIO - PubMed Abstract:
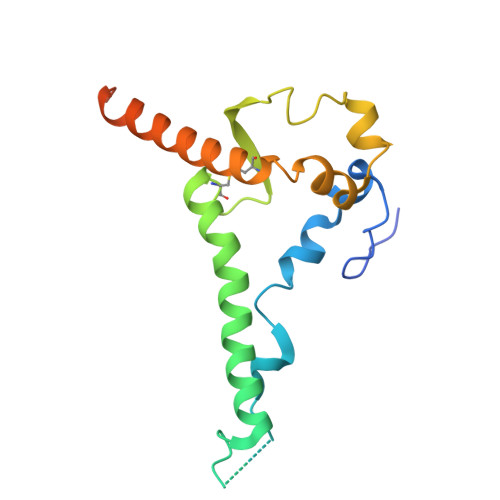
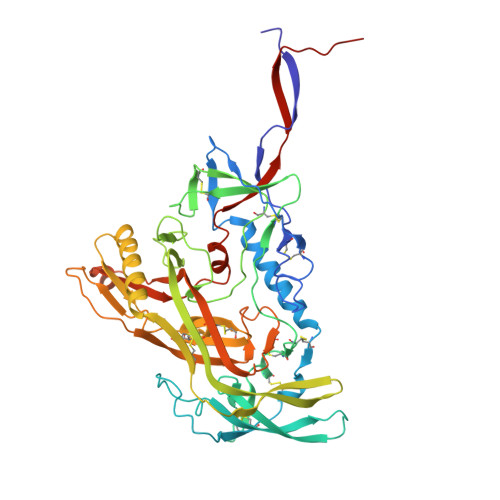
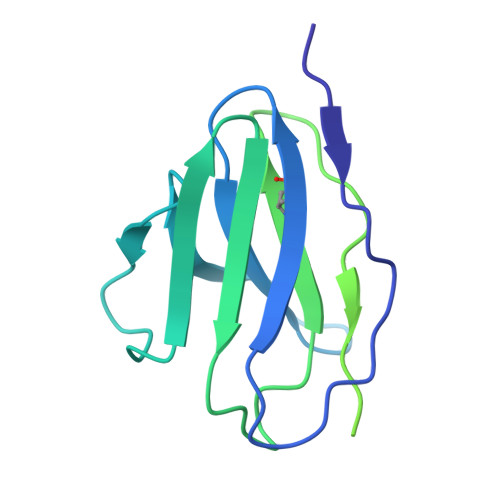
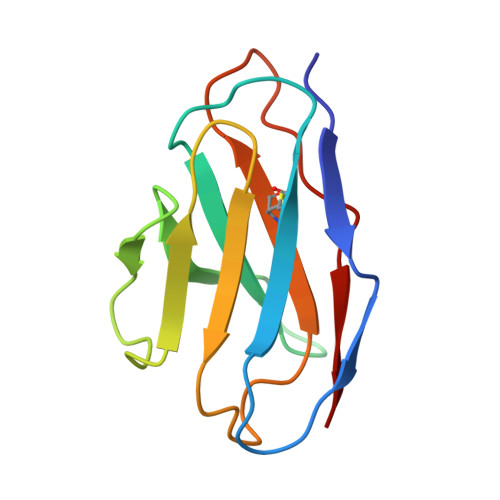
Antibodies that target the gp120-gp41 interface of the HIV-1 envelope (Env) trimer comprise a commonly elicited category of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs). Here, we isolate and characterize VRC44, a bNAb lineage with up to 52% neutralization breadth. The cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of antibody VRC44.01 in complex with the Env trimer reveals binding to the same gp120-gp41 interface site of vulnerability as antibody 35O22 from a different HIV-1-infected donor. In addition to having similar angles of approach and extensive contacts with glycans N88 and N625, VRC44 and 35O22 derive from the same IGHV1-18 gene and share convergent mutations, indicating these two antibodies to be members of the only known highly glycan-dependent multidonor class. Strikingly, both lineages achieved almost 100% neutralization breadth against virus strains displaying high-mannose glycans. The high breadth and reproducible elicitation of VRC44 and 35O22 lineages validate germline-based methods of immunogen design for targeting the HIV-1 gp120-gp41 interface.
- Vaccine Research Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: