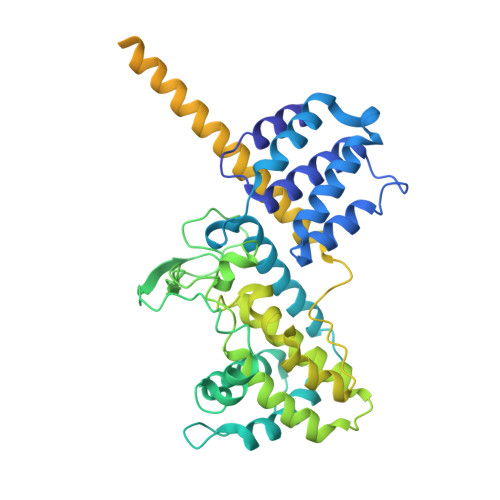
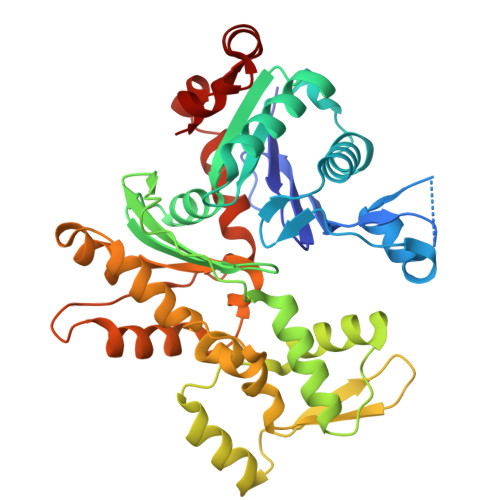
Cryo-EM Detection of AMPylated Histidine Implies Covalent Catalysis in AMPylation Mediated by a Bacterial Effector.
Zhang, Z., Patel, R., Luo, Z.Q., Das, C.(2024) J Mol Biology 437: 168917-168917
- PubMed: 39694182
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168917
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9B2Z - PubMed Abstract:
AMPylation is a post-translational modification (PTM) whereby adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is transferred onto protein hydroxyl groups of serine, threonine, or tyrosine. Recently, an actin-dependent AMPylase namely LnaB from the bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila was found to AMPylate phosphate groups of phosphoribosylated ubiquitin and Src family kinases. LnaB represents an evolutionarily distinct family of AMPylases with conserved active site Ser-His-Glu residues. Here, we capture the structure of the LnaB-actin complex in a putative intermediate state via single-particle cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and find that the catalytic histidine of LnaB is covalently attached to AMP through a phosphoramidate linkage at the Nδ1 atom. This observation provides direct structural evidence of histidine AMPylation as a PTM and implies the possibility of covalent catalysis in LnaB-mediated AMPylation, a mechanism distinct from known AMPylases. Subsequent biochemical studies confirm the observed AMP binding site and provide additional insights into the catalytic properties of LnaB. Together, our work highlights the power of cryo-EM in capturing labile PTMs and transient species during enzymatic reactions, while opening new avenues of mechanistic investigation into the LnaB family.
- Department of Chemistry, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: