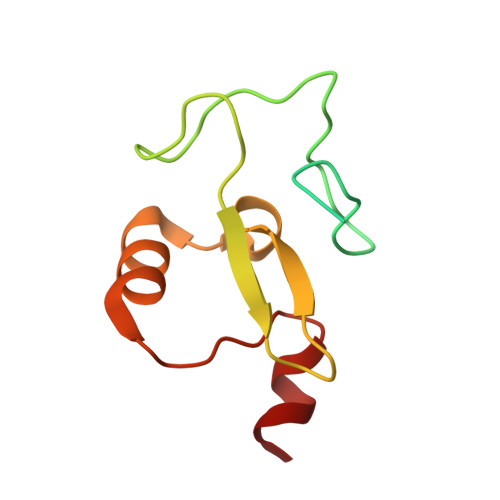
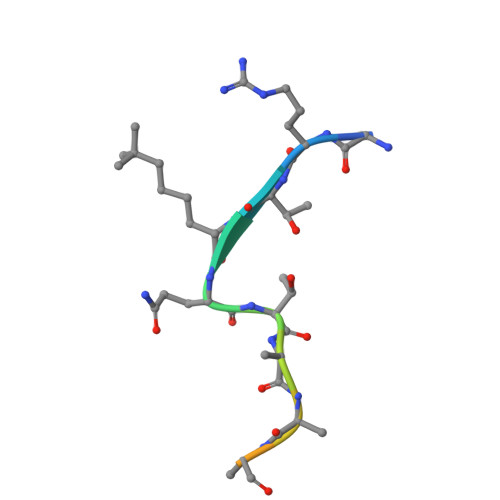
Trimethyllysine Reader Proteins Exhibit Widespread Charge-Agnostic Binding via Different Mechanisms to Cationic and Neutral Ligands.
Travis, C.R., Kean, K.M., Albanese, K.I., Henriksen, H.C., Treacy, J.W., Chao, E.Y., Houk, K.N., Waters, M.L.(2024) J Am Chem Soc 146: 3086-3093
- PubMed: 38266163
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c10031
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8T4R - PubMed Abstract:
In the last 40 years, cation-π interactions have become part of the lexicon of noncovalent forces that drive protein binding. Indeed, tetraalkylammoniums are universally bound by aromatic cages in proteins, suggesting that cation-π interactions are a privileged mechanism for binding these ligands. A prominent example is the recognition of histone trimethyllysine (Kme3) by the conserved aromatic cage of reader proteins, dictating gene expression. However, two proteins have recently been suggested as possible exceptions to the conventional understanding of tetraalkylammonium recognition. To broadly interrogate the role of cation-π interactions in protein binding interactions, we report the first large-scale comparative evaluation of reader proteins for a neutral Kme3 isostere, experimental and computational mechanistic studies, and structural analysis. We find unexpected widespread binding of readers to a neutral isostere with the first examples of readers that bind the neutral isostere more tightly than Kme3. We find that no single factor dictates the charge selectivity, demonstrating the challenge of predicting such interactions. Further, readers that bind both cationic and neutral ligands differ in mechanism: binding Kme3 via cation-π interactions and the neutral isostere through the hydrophobic effect in the same aromatic cage. This discovery explains apparently contradictory results in previous studies, challenges traditional understanding of molecular recognition of tetraalkylammoniums by aromatic cages in myriad protein-ligand interactions, and establishes a new framework for selective inhibitor design by exploiting differences in charge dependence.
- Department of Chemistry, CB 3290, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: