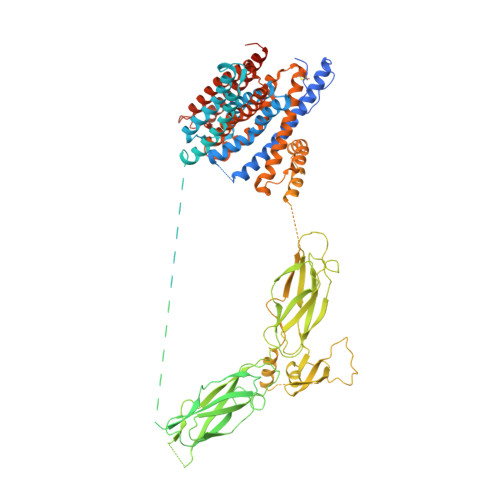
Structural mechanisms of the human cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger NCX1.
Xue, J., Zeng, W., Han, Y., John, S., Ottolia, M., Jiang, Y.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 6181-6181
- PubMed: 37794011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41885-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SGJ, 8SGT - PubMed Abstract:
Na + /Ca 2+ exchangers (NCX) transport Ca 2+ in or out of cells in exchange for Na + . They are ubiquitously expressed and play an essential role in maintaining cytosolic Ca 2+ homeostasis. Although extensively studied, little is known about the global structural arrangement of eukaryotic NCXs and the structural mechanisms underlying their regulation by various cellular cues including cytosolic Na + and Ca 2+ . Here we present the cryo-EM structures of human cardiac NCX1 in both inactivated and activated states, elucidating key structural elements important for NCX ion exchange function and its modulation by cytosolic Ca 2+ and Na + . We demonstrate that the interactions between the ion-transporting transmembrane (TM) domain and the cytosolic regulatory domain define the activity of NCX. In the inward-facing state with low cytosolic [Ca 2+ ], a TM-associated four-stranded β-hub mediates a tight packing between the TM and cytosolic domains, resulting in the formation of a stable inactivation assembly that blocks the TM movement required for ion exchange function. Ca 2+ binding to the cytosolic second Ca 2+ -binding domain (CBD2) disrupts this inactivation assembly which releases its constraint on the TM domain, yielding an active exchanger. Thus, the current NCX1 structures provide an essential framework for the mechanistic understanding of the ion transport and cellular regulation of NCX family proteins.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Physiology, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: