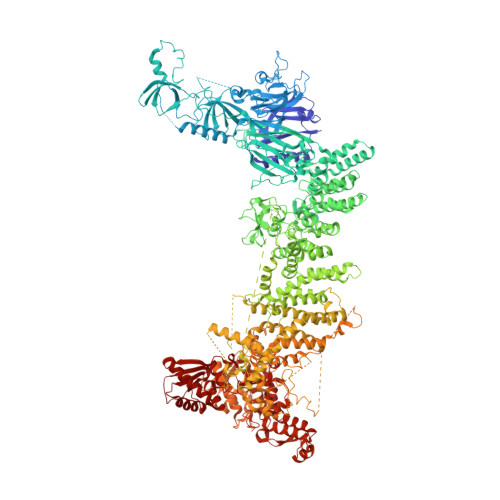
UBR5 forms ligand-dependent complexes on chromatin to regulate nuclear hormone receptor stability.
Tsai, J.M., Aguirre, J.D., Li, Y.D., Brown, J., Focht, V., Kater, L., Kempf, G., Sandoval, B., Schmitt, S., Rutter, J.C., Galli, P., Sandate, C.R., Cutler, J.A., Zou, C., Donovan, K.A., Lumpkin, R.J., Cavadini, S., Park, P.M.C., Sievers, Q., Hatton, C., Ener, E., Regalado, B.D., Sperling, M.T., Slabicki, M., Kim, J., Zon, R., Zhang, Z., Miller, P.G., Belizaire, R., Sperling, A.S., Fischer, E.S., Irizarry, R., Armstrong, S.A., Thoma, N.H., Ebert, B.L.(2023) Mol Cell 83: 2753
- PubMed: 37478846
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.06.028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8P82, 8P83 - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear hormone receptors (NRs) are ligand-binding transcription factors that are widely targeted therapeutically. Agonist binding triggers NR activation and subsequent degradation by unknown ligand-dependent ubiquitin ligase machinery. NR degradation is critical for therapeutic efficacy in malignancies that are driven by retinoic acid and estrogen receptors. Here, we demonstrate the ubiquitin ligase UBR5 drives degradation of multiple agonist-bound NRs, including the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA), retinoid x receptor alpha (RXRA), glucocorticoid, estrogen, liver-X, progesterone, and vitamin D receptors. We present the high-resolution cryo-EMstructure of full-length human UBR5 and a negative stain model representing its interaction with RARA/RXRA. Agonist ligands induce sequential, mutually exclusive recruitment of nuclear coactivators (NCOAs) and UBR5 to chromatin to regulate transcriptional networks. Other pharmacological ligands such as selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) degrade their receptors through differential recruitment of UBR5 or RNF111. We establish the UBR5 transcriptional regulatory hub as a common mediator and regulator of NR-induced transcription.
- Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA; Division of Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA; Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: