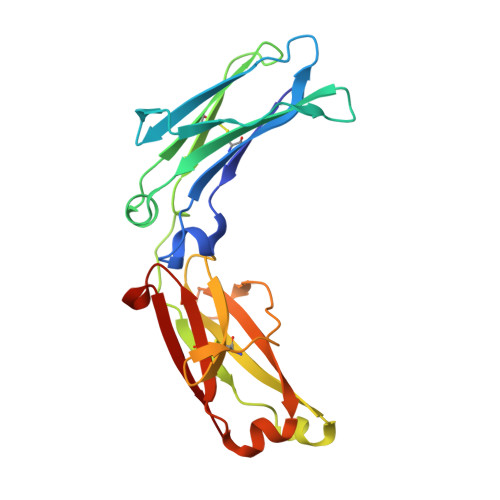
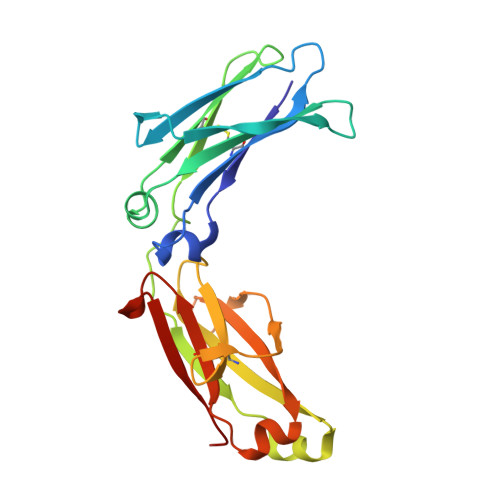
Complement is activated by elevated IgG3 hexameric platforms and deposits C4b onto distinct antibody domains.
Abendstein, L., Dijkstra, D.J., Tjokrodirijo, R.T.N., van Veelen, P.A., Trouw, L.A., Hensbergen, P.J., Sharp, T.H.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 4027-4027
- PubMed: 37419978
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39788-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BTB - PubMed Abstract:
IgG3 is unique among the IgG subclasses due to its extended hinge, allotypic diversity and enhanced effector functions, including highly efficient pathogen neutralisation and complement activation. It is also underrepresented as an immunotherapeutic candidate, partly due to a lack of structural information. Here, we use cryoEM to solve structures of antigen-bound IgG3 alone and in complex with complement components. These structures reveal a propensity for IgG3-Fab clustering, which is possible due to the IgG3-specific flexible upper hinge region and may maximise pathogen neutralisation by forming high-density antibody arrays. IgG3 forms elevated hexameric Fc platforms that extend above the protein corona to maximise binding to receptors and the complement C1 complex, which here adopts a unique protease conformation that may precede C1 activation. Mass spectrometry reveals that C1 deposits C4b directly onto specific IgG3 residues proximal to the Fab domains. Structural analysis shows this to be caused by the height of the C1-IgG3 complex. Together, these data provide structural insights into the role of the unique IgG3 extended hinge, which will aid the development and design of upcoming immunotherapeutics based on IgG3.
- Department of Cell and Chemical Biology, Leiden University Medical Center, 2300 RC, Leiden, The Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: