Structural basis for different membrane-binding properties of E. coli anaerobic and human mitochondrial beta-oxidation trifunctional enzymes.
Sah-Teli, S.K., Pinkas, M., Hynonen, M.J., Butcher, S.J., Wierenga, R.K., Novacek, J., Venkatesan, R.(2023) Structure 31: 812
- PubMed: 37192613
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2023.04.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BNR, 8BNU, 8BRJ - PubMed Abstract:
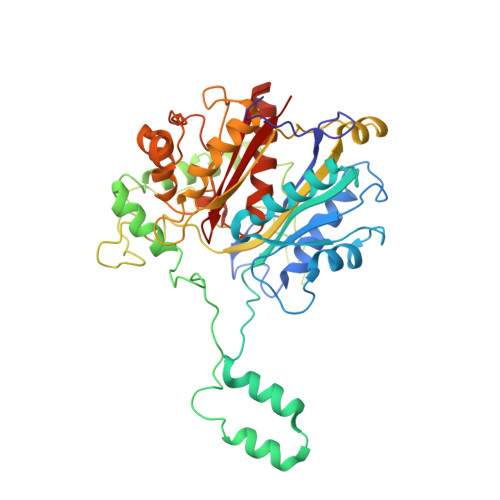
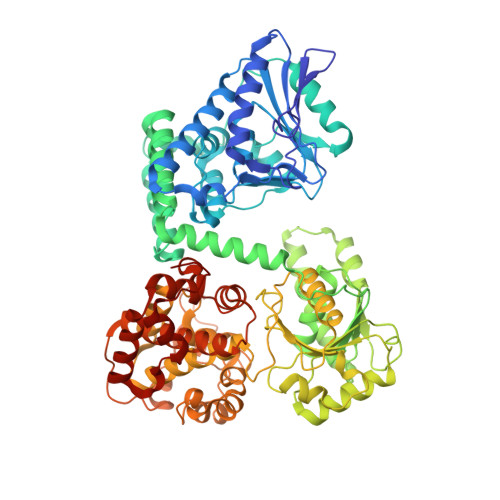
Facultative anaerobic bacteria such as Escherichia coli have two α 2 β 2 heterotetrameric trifunctional enzymes (TFE), catalyzing the last three steps of the β-oxidation cycle: soluble aerobic TFE (EcTFE) and membrane-associated anaerobic TFE (anEcTFE), closely related to the human mitochondrial TFE (HsTFE). The cryo-EM structure of anEcTFE and crystal structures of anEcTFE-α show that the overall assembly of anEcTFE and HsTFE is similar. However, their membrane-binding properties differ considerably. The shorter A5-H7 and H8 regions of anEcTFE-α result in weaker α-β as well as α-membrane interactions, respectively. The protruding H-H region of anEcTFE-β is therefore more critical for membrane-association. Mutational studies also show that this region is important for the stability of the anEcTFE-β dimer and anEcTFE heterotetramer. The fatty acyl tail binding tunnel of the anEcTFE-α hydratase domain, as in HsTFE-α, is wider than in EcTFE-α, accommodating longer fatty acyl tails, in good agreement with their respective substrate specificities.
- Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of Oulu, 90220 Oulu, Finland.
Organizational Affiliation: