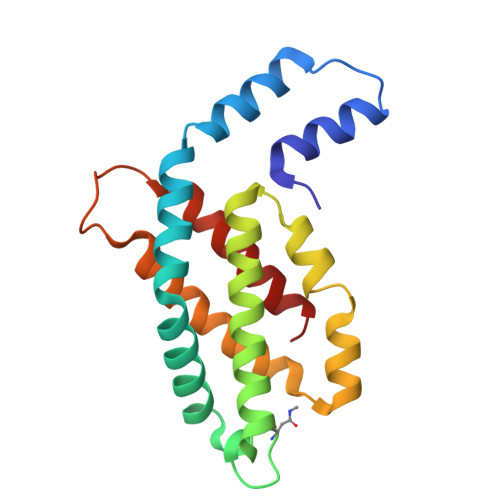
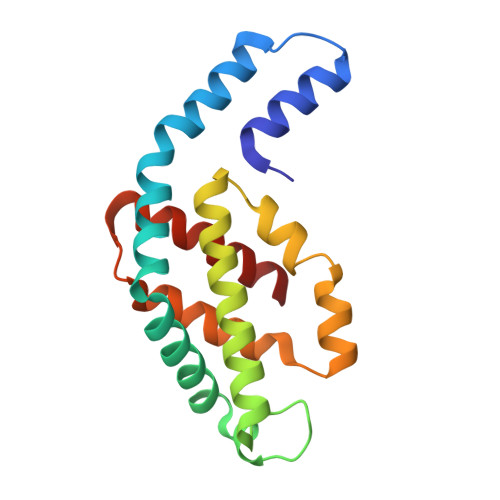
Structure and stability of phycocyanin from thermotolerant Oscillatoria.
Patel, S.N., Sonani, R.R., Gupta, G.D., Singh, N.K., Upadhyaya, C., Sonavane, B., Amin, S., Kumar, V., Madamwar, D.(2025) FEBS Lett 599: 1420-1432
- PubMed: 40297916
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.70048
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Z20 - PubMed Abstract:
Phycocyanin (PC), a pigment-protein complex with diverse biotechnological applications, plays a key role in light energy transfer for photosynthesis in cyanobacteria. PC (O-PC) from a thermotolerant cyanobacteria Oscillatoria sp. N09DM exhibits remarkable stability compared to its mesophilic counterparts, making it highly valuable for industrial and medical applications. To understand the basis of its stability, the crystal structure of O-PC is solved and analysed. Structural analysis reveals a key molecular interaction, including hydrogen bonds, salt bridges and hydrophobic interactions, along with amino acid substitutions that provide the thermal stability. Additionally, structural results provide insights into chromophore-protein interactions for understanding O-PC's role in the efficient transfer of light energy.
- P. D. Patel Institute of Applied Sciences, Charotar University of Science and Technology, Changa, Anand, Gujarat, India.
Organizational Affiliation: