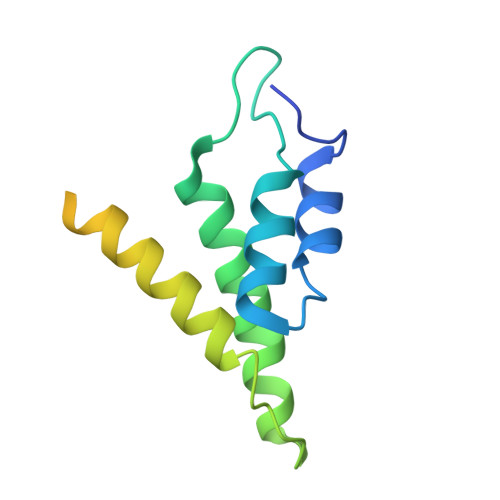
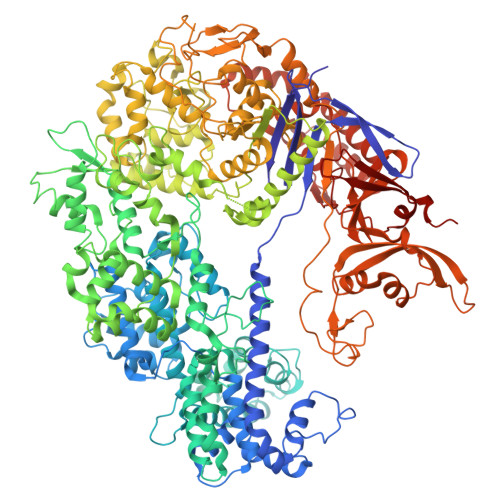
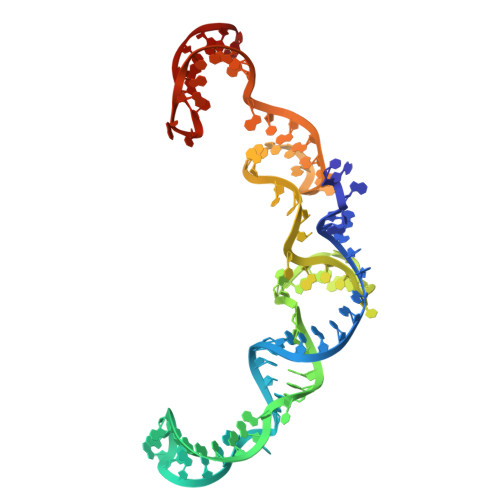
Inhibition mechanisms of CRISPR-Cas9 by AcrIIA25.1 and AcrIIA32.
Zheng, J., Zhu, Y., Huang, T., Gao, W., He, J., Huang, Z.(2024) Sci China Life Sci 67: 1781-1791
- PubMed: 38842649
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-024-2607-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YE6, 8YE9 - PubMed Abstract:
In the ongoing arms race between bacteria and bacteriophages, bacteriophages have evolved anti-CRISPR proteins to counteract bacterial CRISPR-Cas systems. Recently, AcrIIA25.1 and AcrIIA32 have been found to effectively inhibit the activity of SpyCas9 both in bacterial and human cells. However, their molecular mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of ternary complexes formed by AcrIIA25.1 and AcrIIA32 bound to SpyCas9-sgRNA. Using structural analysis and biochemical experiments, we revealed that AcrIIA25.1 and AcrIIA32 recognize a novel, previously-unidentified anti-CRISPR binding site on SpyCas9. We found that both AcrIIA25.1 and AcrIIA32 directly interact with the WED domain, where they spatially obstruct conformational changes of the WED and PI domains, thereby inhibiting SpyCas9 from recognizing protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) and unwinding double-stranded DNA. In addition, they may inhibit nuclease activity by blocking the dynamic conformational changes of the SpyCas9 surveillance complex. In summary, our data elucidate the inhibition mechanisms of two new anti-CRISPR proteins, provide new strategies for the modulation of SpyCas9 activity, and expand our understanding of the diversity of anti-CRISPR protein inhibition mechanisms.
- HIT Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150080, China.
Organizational Affiliation: