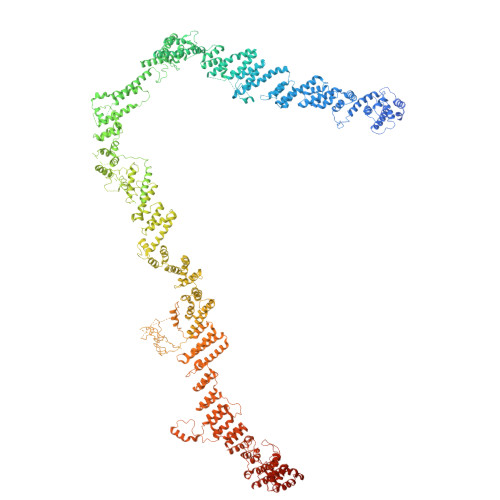
Structural basis for membrane remodeling by the AP5-SPG11-SPG15 complex.
Mai, X., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Liu, M., Teng, F., Liu, Z., Su, M.Y., Stjepanovic, G.(2025) Nat Struct Mol Biol 32: 1334-1346
- PubMed: 40175557
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-025-01500-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YAB, 8YAD, 8YAH - PubMed Abstract:
The human spastizin (spastic paraplegia 15, SPG15) and spatacsin (spastic paraplegia 11, SPG11) complex is involved in the formation of lysosomes, and mutations in these two proteins are linked with hereditary autosomal-recessive spastic paraplegia. SPG11-SPG15 can cooperate with the fifth adaptor protein complex (AP5) involved in membrane sorting of late endosomes. We employed cryogenic-electron microscopy and in silico predictions to investigate the structural assemblies of the SPG11-SPG15 and AP5-SPG11-SPG15 complexes. The W-shaped SPG11-SPG15 intertwined in a head-to-head fashion, and the N-terminal region of SPG11 is required for AP5 complex interaction and assembly. The AP5 complex is in a super-open conformation. Our findings reveal that the AP5-SPG11-SPG15 complex can bind PI3P molecules, sense membrane curvature and drive membrane remodeling in vitro. These studies provide insights into the structure and function of the spastic paraplegia AP5-SPG11-SPG15 complex, which is essential for the initiation of autolysosome tubulation.
- Kobilka Institute of Innovative Drug Discovery, School of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
Organizational Affiliation: