Selective targeting of oncogenic hotspot mutations of the HER2 extracellular domain.
Bang, I., Hattori, T., Leloup, N., Corrado, A., Nyamaa, A., Koide, A., Geles, K., Buck, E., Koide, S.(2025) Nat Chem Biol 21: 706-715
- PubMed: 39438724
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-024-01751-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VQD, 8VQE - PubMed Abstract:
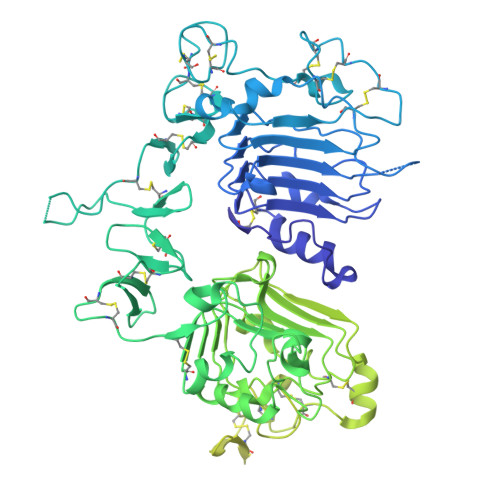
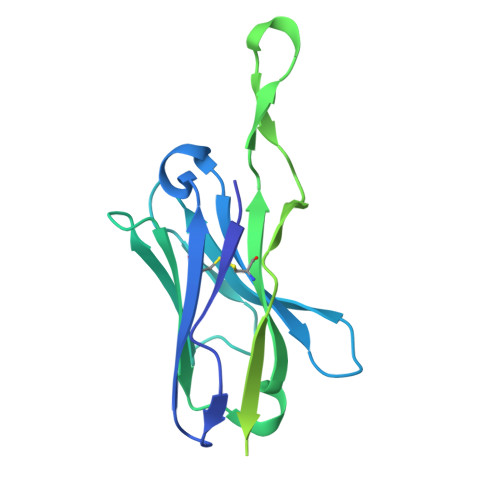
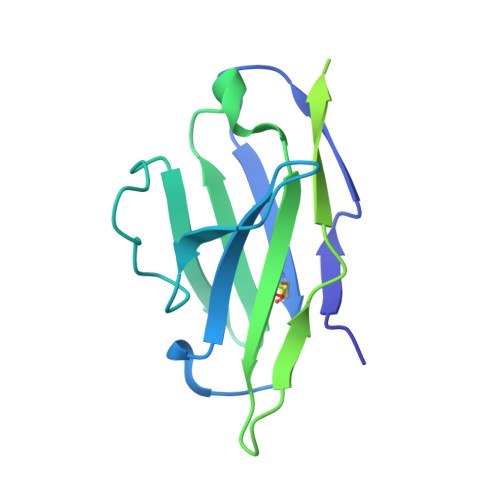
Oncogenic mutations in the extracellular domain (ECD) of cell-surface receptors could serve as tumor-specific antigens that are accessible to antibody therapeutics. Such mutations have been identified in receptor tyrosine kinases including HER2. However, it is challenging to selectively target a point mutant, while sparing the wild-type protein. Here we developed antibodies selective to HER2 S310F and S310Y, the two most common oncogenic mutations in the HER2 ECD, via combinatorial library screening and structure-guided design. Cryogenic-electron microscopy structures of the HER2 S310F homodimer and an antibody bound to HER2 S310F revealed that these antibodies recognize the mutations in a manner that mimics the dimerization arm of HER2 and thus inhibit HER2 dimerization. These antibodies as T cell engagers selectively killed a HER2 S310F-driven cancer cell line in vitro, and in vivo as a xenograft. These results validate HER2 ECD mutations as actionable therapeutic targets and offer promising candidates toward clinical development.
- Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York University Langone Health, New York, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: