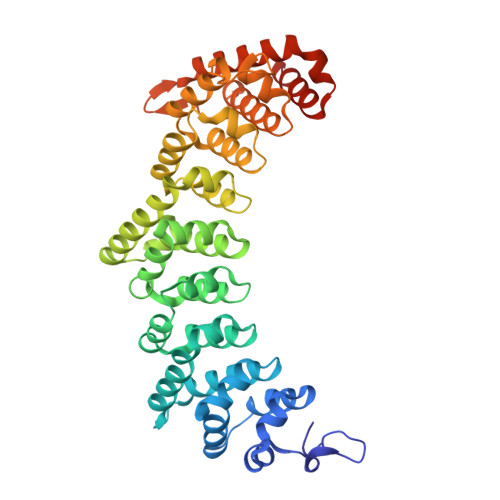
A higher order PUF complex is central to regulation of C. elegans germline stem cells.
Qiu, C., Crittenden, S.L., Carrick, B.H., Dillard, L.B., Costa Dos Santos, S.J., Dandey, V.P., Dutcher, R.C., Viverette, E.G., Wine, R.N., Woodworth, J., Campbell, Z.T., Wickens, M., Borgnia, M.J., Kimble, J., Hall, T.M.T.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 123-123
- PubMed: 39747099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55526-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VIV - PubMed Abstract:
PUF RNA-binding proteins are broadly conserved stem cell regulators. Nematode PUF proteins maintain germline stem cells (GSCs) and, with key partner proteins, repress differentiation mRNAs, including gld-1. Here we report that PUF protein FBF-2 and its partner LST-1 form a ternary complex that represses gld-1 via a pair of adjacent FBF binding elements (FBEs) in its 3'UTR. One LST-1 molecule links two FBF-2 molecules via motifs in the LST-1 intrinsically-disordered region; the gld-1 FBE pair includes a well-established 'canonical' FBE and a newly-identified noncanonical FBE. Remarkably, this FBE pair drives both full RNA repression in GSCs and full RNA activation upon differentiation. Discoveries of the LST-1-FBF-2 ternary complex, the gld-1 adjacent FBEs, and their in vivo significance predict an expanded regulatory repertoire of different assemblies of PUF-partner-RNA higher order complexes in nematode GSCs. This also suggests analogous PUF controls may await discovery in other biological contexts and organisms.
- Epigenetics and RNA Biology Laboratory, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: