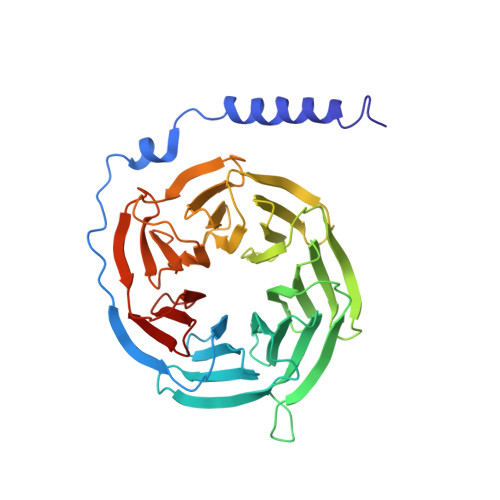
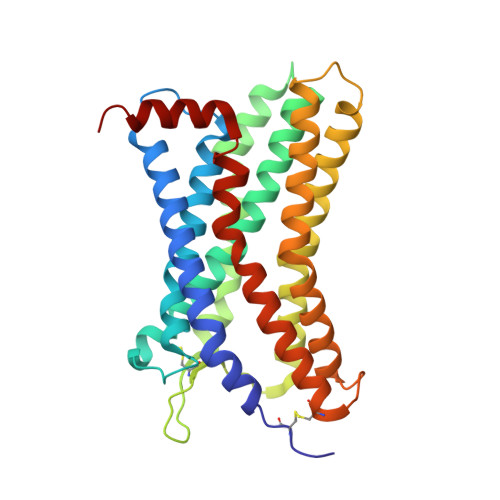
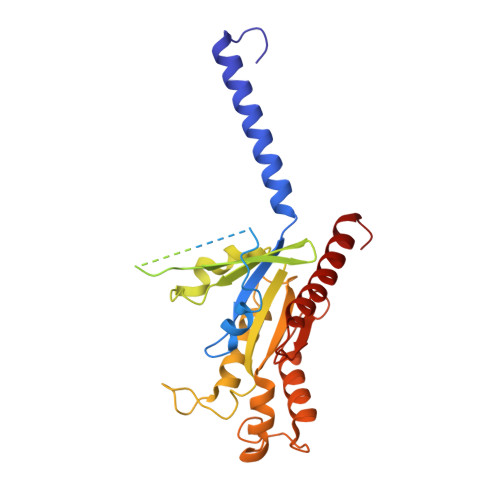
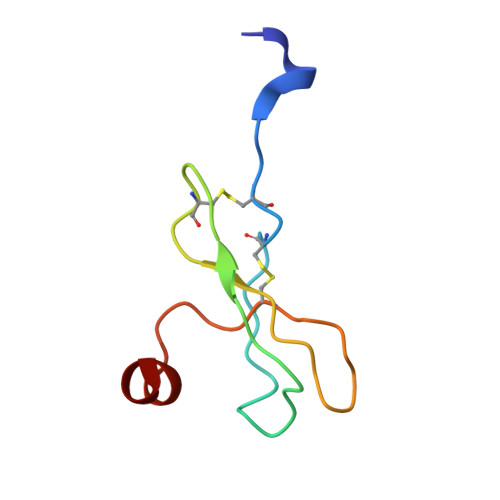
Cryo-EM structure of monomeric CXCL12-bound CXCR4 in the active state.
Liu, Y., Liu, A., Li, X., Liao, Q., Zhang, W., Zhu, L., Ye, R.D.(2024) Cell Rep 43: 114578-114578
- PubMed: 39093700
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114578
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8K3Z - PubMed Abstract:
CXCR4 binding of its endogenous agonist CXCL12 leads to diverse functions, including bone marrow retention of hematopoietic progenitors and cancer metastasis. However, the structure of the CXCL12-bound CXCR4 remains unresolved despite available structures of CXCR4 in complex with antagonists. Here, we present the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the CXCL12-CXCR4-Gi complex at an overall resolution of 2.65 Å. CXCL12 forms a 1:1 stoichiometry complex with CXCR4, following the two-site model. The first 8 amino acids of mature CXCL12 are crucial for CXCR4 activation by forming polar interactions with minor sub-pocket residues in the transmembrane binding pocket. The 3.2-Å distance between V3 of CXCL12 and the "toggle switch" W 6.48 marks the deepest insertion among all chemokine-receptor pairs, leading to conformational changes of CXCR4 for G protein activation. These results, combined with functional assays and computational analysis, provide the structural basis for CXCR4 activation by CXCL12.
- Kobilka Institute of Innovative Drug Discovery, School of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518172, China.
Organizational Affiliation: