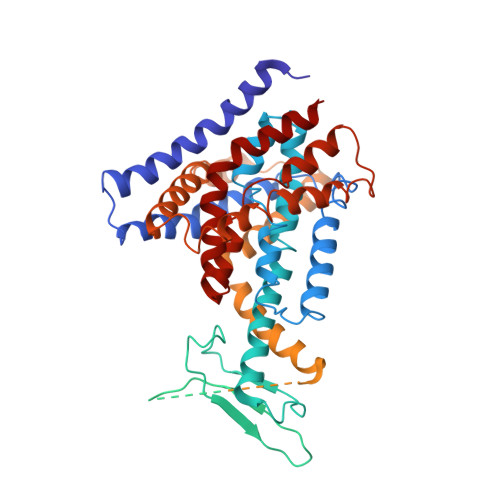
Chemical inhibition of Arabidopsis PIN-FORMED auxin transporters by the anti-inflammatory drug naproxen.
Xia, J., Kong, M., Yang, Z., Sun, L., Peng, Y., Mao, Y., Wei, H., Ying, W., Gao, Y., Friml, J., Weng, J., Liu, X., Sun, L., Tan, S.(2023) Plant Commun 4: 100632-100632
- PubMed: 37254481
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100632
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JH5 - PubMed Abstract:
The phytohormone auxin plays central roles in many growth and developmental processes in plants. Development of chemical tools targeting the auxin pathway is useful for both plant biology and agriculture. Here we reveal that naproxen, a synthetic compound with anti-inflammatory activity in humans, acts as an auxin transport inhibitor targeting PIN-FORMED (PIN) transporters in plants. Physiological experiments indicate that exogenous naproxen treatment affects pleiotropic auxin-regulated developmental processes. Additional cellular and biochemical evidence indicates that naproxen suppresses auxin transport, specifically PIN-mediated auxin efflux. Moreover, biochemical and structural analyses confirm that naproxen binds directly to PIN1 protein via the same binding cavity as the indole-3-acetic acid substrate. Thus, by combining cellular, biochemical, and structural approaches, this study clearly establishes that naproxen is a PIN inhibitor and elucidates the underlying mechanisms. Further use of this compound may advance our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of PIN-mediated auxin transport and expand our toolkit in auxin biology and agriculture.
- MOE Key Laboratory for Cellular Dynamics, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Biomedical Sciences and Health Laboratory of Anhui Province, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China.
Organizational Affiliation: