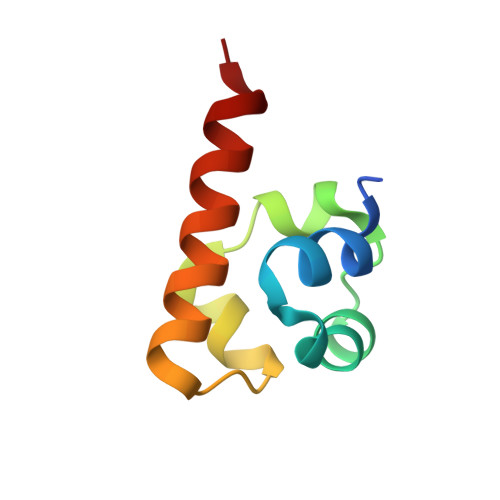
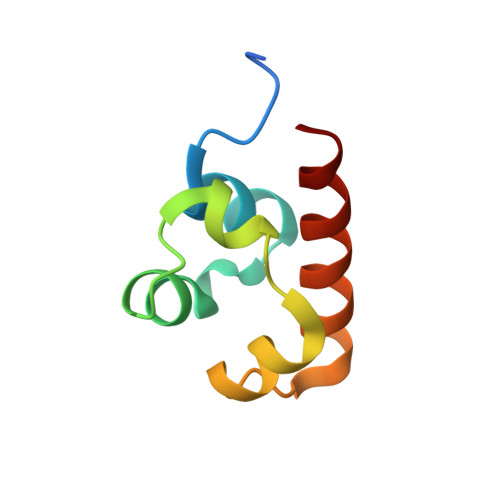
SASH1: A Novel Eph Receptor Partner and Insights into SAM-SAM Interactions.
Ding, Y., Chen, Q., Shan, H., Liu, J., Lv, C., Wang, Y., Yuan, L., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Yin, Y., Xiao, K., Li, J., Liu, W.(2023) J Mol Biology 435: 168243-168243
- PubMed: 37619706
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168243
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8J1I - PubMed Abstract:
The Eph (erythropoietin-producing human hepatocellular) receptor family, the largest subclass of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), plays essential roles in embryonic development and neurogenesis. The intracellular Sterile Alpha Motif (SAM) domain presents a critical structural feature that distinguishes Eph receptors from other RTKs and participates in recruiting and binding downstream molecules. This study identified SASH1 (SAM and SH3 domain containing 1) as a novel Eph receptor-binding partner through SAM-SAM domain interactions. Our comprehensive biochemical analyses revealed that SASH1 selectively interacts with Eph receptors via its SAM1 domain, displaying the highest affinity for EphA8. The high-resolution crystal structure of the EphA8-SASH1 complex provided insights into the specific intermolecular interactions between these proteins. Cellular assays confirmed that EphA8 and SASH1 co-localize and co-precipitate in mammalian cells, with cancer mutations (EphA8 R942H or G978D) impairing this interaction. We demonstrated that SAM-SAM interaction is critical for SASH1-mediated regulation of EphA8 kinase activity, shedding new light on the Eph signaling pathway and expanding our understanding of the molecular basis of the tumor suppressor gene SASH1.
- Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Neuronal Structural Biology, Biomedical Research Institute, Shenzhen Peking University-The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Medical Center, Shenzhen 518036, China. Electronic address: https://twitter.com/dingyuzhen8.
Organizational Affiliation: